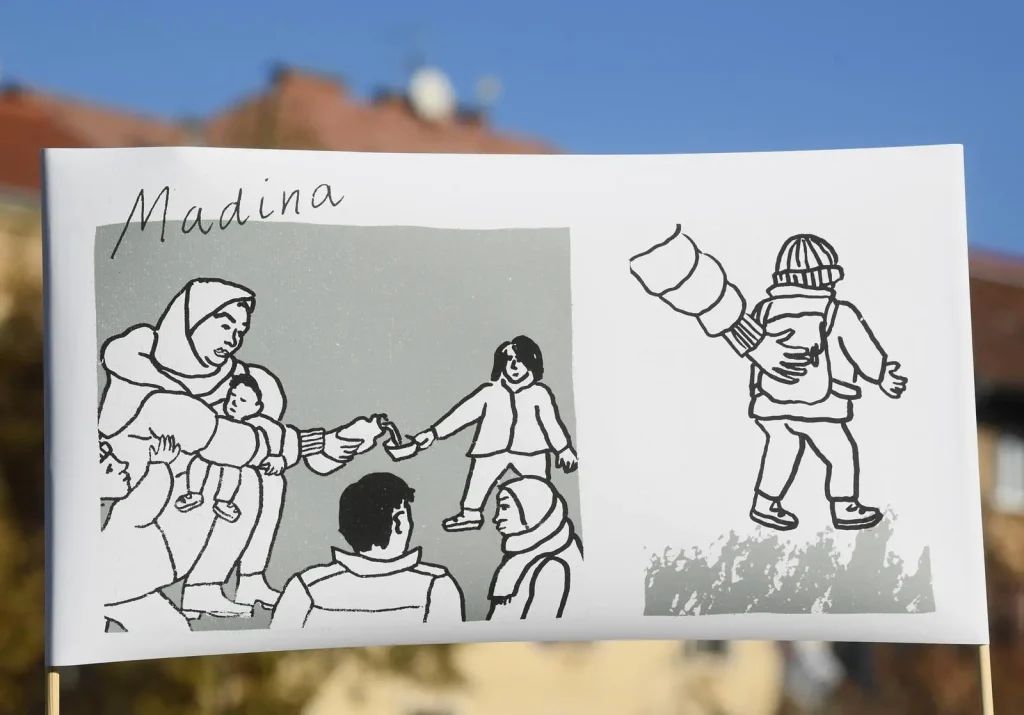
Ombudswoman Tena Šimonovic Einwalter said in an interview with Hina that, following the ruling of the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) in the death of Madina Hosseini, it is important to change the system because ”as a state we want to respect human rights. This is the complete opposite of what Prime Minister Andrej Plenković and the Croatian representative in the Strasbourg court, Štefica Stažnik, claim”. Namely, they both assure that this is not a systemic problem, because Croatia has not been declared responsible for the death of little Madina, but for an ineffective investigation into her death.
The six-year-old girl, Madina Hosseini was killed in November 2017 when she was hit by a train on the Croatian-Serbian border after her family had allegedly been denied the opportunity to seek asylum by Croatian authorities and were ordered to return to Serbia via the tracks.
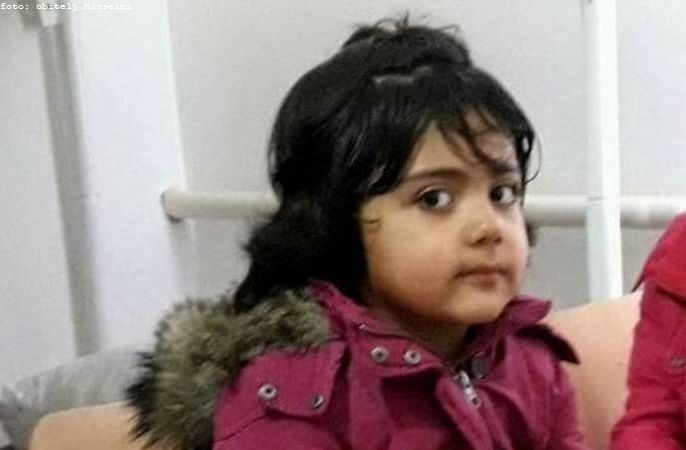

Madina Hosseini (Photo: Family album)
The ECtHR confirmed that in Madina’s case, Croatia had violated rights under the European Convention on Human Rights. As stated in the verdict, Madina’s right to life, humiliated her family’s children by keeping them in custody, illegally deprived the whole family of their liberty, and collectively expelled part of the family from Croatia and denied them access to a lawyer.
Why is this verdict significant?
In an interview with Hina, Ombudswoman Tena Šimonović Einwalter commented on the significance of the verdict itself and the moves that Croatia needs to make in order to execute the verdict of that court.
Speaking about the human rights situation, Šimonović Einwalter announced that, in addition to the annual report already published, she would soon present a special report to the Croatian Parliament on the impact of the epidemic in the last two years on human rights and equality.
HINA: The ECtHR passed a verdict deciding in this particular case, but can it be said that it also said that Croatia is systematically violating the rights of refugees at the borders?
ŠIMONOVIC EINWALTER: It is difficult for the ECHR to say that in that way, in those words. This verdict addresses the issue of the treatment of Madina’s family, in this specific situation. But the court also says that the case “raises several important issues about migration control by the Croatian authorities” and that “the impact of this case goes beyond the special situation of the family”. The court also took into account a number of earlier allegations of violations of migrants’ rights.
Some sentences from the decision, it seems to me, therefore indicate that the impact of the case goes beyond this particular family situation and I think it is good to read it that way if we want changes. It is important to carefully analyze and seriously implement this court decision and change the system because as a state we want to respect national law, European law, international law, and human rights. Is there the will to do it? I really hope so.
HINA: The court found that the convention had been violated because the police at the border did not assess the individual situation of the refugee family before they were deported to Serbia. It did not accept the state’s argument that the refugee family was crossing the border illegally. What does this mean now, since the beginning of that refugee crisis, it has been persistently emphasized that we are “defending” ourselves at the borders from those who break the law by crossing them?
ŠIMONOVIĆ EINWALTER: In fact, the legal situation was clear even before this decision. It is often pointed out that the police should guard the border, that illegal crossing of the state border is prohibited, and that is exactly what the law says. At the same time, it is legally defined that persons have the right to seek international protection, regardless of the manner of entry into the country. Therefore, there must be an individualized procedure. It includes, because of the risk of violating international law, the possibility that people who are in a specific situation because of fleeing war and exposure to practices such as torture or the death penalty in their countries of origin have the right to seek international protection. It is also needed by people who are victims of human trafficking, rape, or severe violence.
You can’t know if that person will have the right to asylum without conducting a procedure – to ask who that person is, where he is fleeing from and why, it is not written on anyone’s forehead. As a first contact, officials should try to identify vulnerable people who may want to apply for international protection.
This is a matter of individualized approach, where special vulnerability is sometimes visible at first, for example in children or unaccompanied children, and the best interests of the child must take precedence.
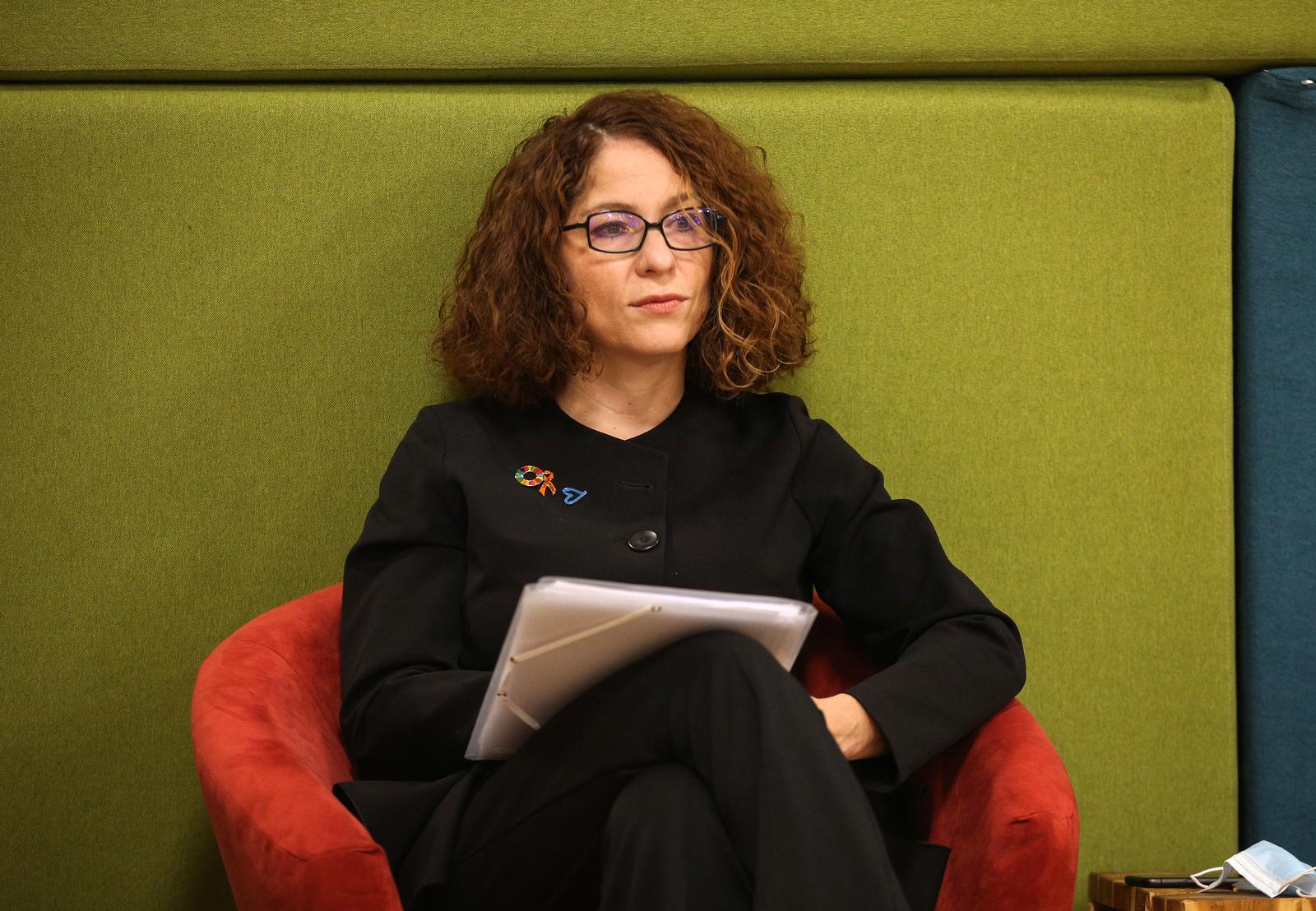

Tena Šimonović Einwalter (Photo: Zeljko Hladika/PIXSELL)
HINA: In the next six months, Croatia must conduct an effective investigation into Madina’s death, but also draw up an action plan to eliminate the violations identified by the court. Will this change the situation and the protocol for treating refugees?
ŠIMONOVIĆ EINWALTER: Within six months, but maybe earlier, the Office of the Representative of the Republic of Croatia before the ECtHR must adopt an action plan. In this regard, through a body in which representatives of various institutions participate, we can also give expert opinions and proposals, and it includes ministries, courts, the Constitutional Court, and others. The point of the ECtHR judgments is justice for individuals, but also to change the practice, if necessary the laws, in order to respect the legal standards of human rights protection. It can also be a question of, for example, how to conduct an effective investigation, which was an important issue in this case. We have also heard that Minister Davor Božinović has publicly stated that the responsibility in such cases is on the system and that we need to see what are the things that can and should be corrected.
HINA: Has the Ukrainian crisis shown that those fleeing the war can be treated differently?
ŠIMONOVIĆ EINWALTER: We are currently witnessing great solidarity of citizens towards Ukrainians, but I would like to remind you that we saw this solidarity of citizens in 2015 as well – and then many were ready to help. However, now the European Union has reacted differently than in 2015. The Temporary Protection Directive existed even then, and could theoretically be activated. It is a political decision at the EU level.
With the recent activation of the directive, IDPs from Ukraine have a much simpler and faster procedure. What can be discussed is whether it should have been activated in the past. Could it have been any different for some other people fleeing another war? I believe that a new level of solidarity and assistance to refugees is now being seen. In an ideal world, I would like to see Europe respond in this way to all refugees fleeing the horrors of war.
HINA: Your report makes recommendations on how to address the shortcomings you have identified in the implementation of human rights. Judging by the number, a total of 156 recommendations, a lot of work, what needs to be worked on the most?
ŠIMONOVIĆ EINWALTER: There are many problems, and I would like to point out the problems of access to health care and health services, the need for stronger support and protection of senior citizens, the issue of access to information for citizens regarding rights, and how to exercise them. It is necessary to ensure that the institutions suit them, that the procedures do not take too long, that they are less formalistic, and that their work shows the understanding that they are there for the citizens, to provide them with an easier way to exercise their rights. In some areas, the problems are long-lasting, I have been working in this institution for 14 years and changes are happening slowly.
We also point out systemic problems analytically and comprehensively. What I am always happy about are the improvements, and of course, there are some, especially when fulfilling some of our recommendations, either in an individual case or these systematic ones from the annual report, lead to a higher level of rights for citizens. That is the point of these recommendations. From the Report for 2020, 43 percent of the recommendations were implemented, which is a big jump compared to 2019, when 20 percent of them were implemented. I hope this trend continues.
HINA: In times of insecurity, the most socially vulnerable groups are particularly hard hit. How should the state act on this?
ŠIMONOVIĆ EINWALTER: Those who have been ill before always suffer the most. It will be the same now – it is the poorer senior citizens, but also those who live near the poverty line. Single-parent families and those with three or more children are in a difficult position.
Government measures to alleviate the situation are welcome, but they will certainly not remove all concerns from citizens. It is important to monitor at the state level whether the measures should be corrected, with special attention to the impact on those who find it particularly difficult, and we will monitor this as well.
HINA: A large number of complaints were related to the use of covid certificates and vaccinations. How has the epidemic affected equality and human rights in Croatia?
SIMONOVIC EINWALTER: We have been through a lot in these two years. The epidemic is still actually going on, so while many of us are feeling relieved, no one knows what will happen in the fall. These experiences should be used to learn and strengthen the key sectors: health, social, education, and civil protection. We are currently finalizing a special report on the impact of the epidemic on human rights and equality in those two years, which we will soon submit to Parliament. The purpose of this report is to see what the effects of the epidemic are and how to manage it. It has changed our lives and we need to see what can be done better and differently.
That is why we analyze the impact on certain human rights and certain groups of citizens because some have fared worse. These are the elderly, but they are not the only ones. There is also the impact of poverty and the availability of different services. The fact is that not everyone could be vaccinated, for health reasons, and at the same time, we had the question of the availability of testing, which was not the same for everyone. There are also lessons about informing citizens, given the fake news and misinformation. We will include all of this in the recommendations, and I hope that this report will be the basis for positive progress towards strengthening the resilience of society in the future, to the epidemic, but also to other possible crises.
For more, check out our politics section.