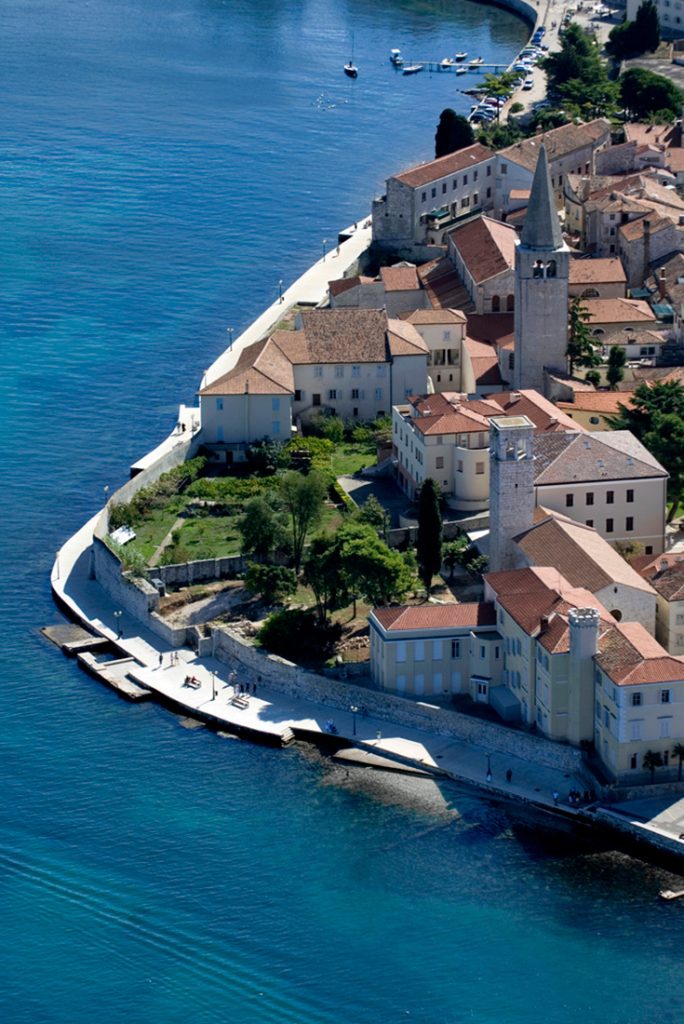
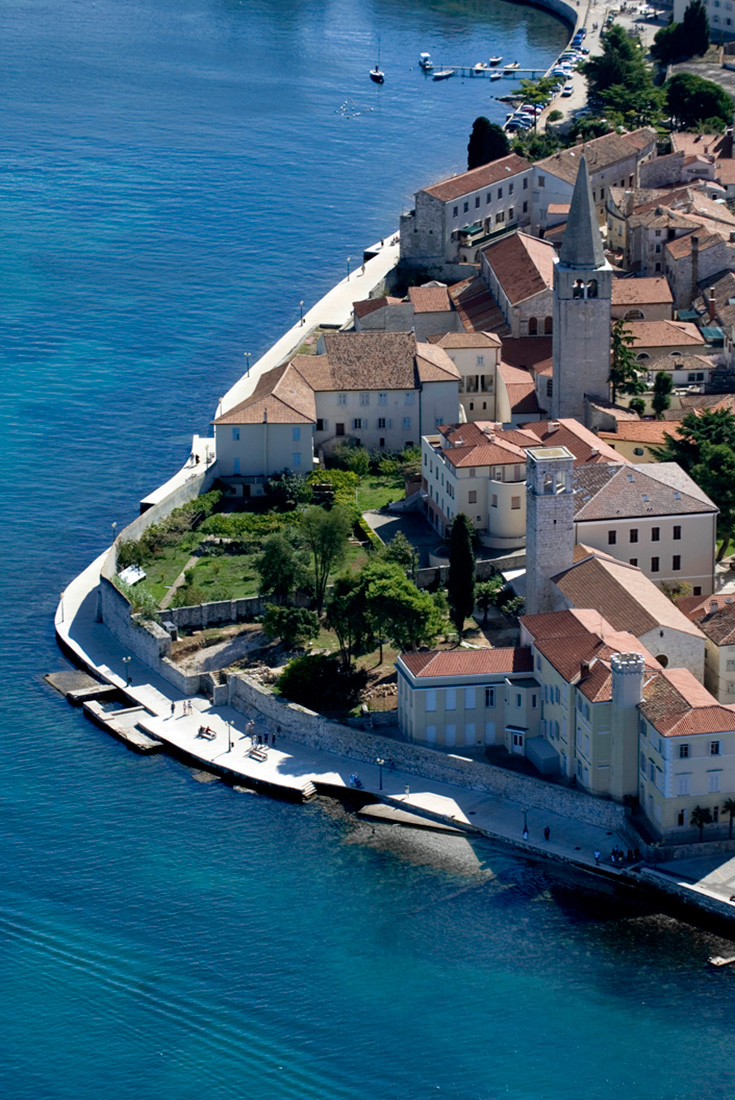
This article will take a look at the Euphrasian Basilica in beautiful Poreč, which is listed on the prestigious UNESCO World Heritage List.
This basilica is extraordinary because it is a truly unique example of early Christian and Byzantine architecture and boasts some spectacular mosaics from that time. This is a complete surviving complex of this type, and this episcopal complex consists of the basilica, the atrium, the baptistery and the episcopal palace, which is an impressive example of religious architecture.
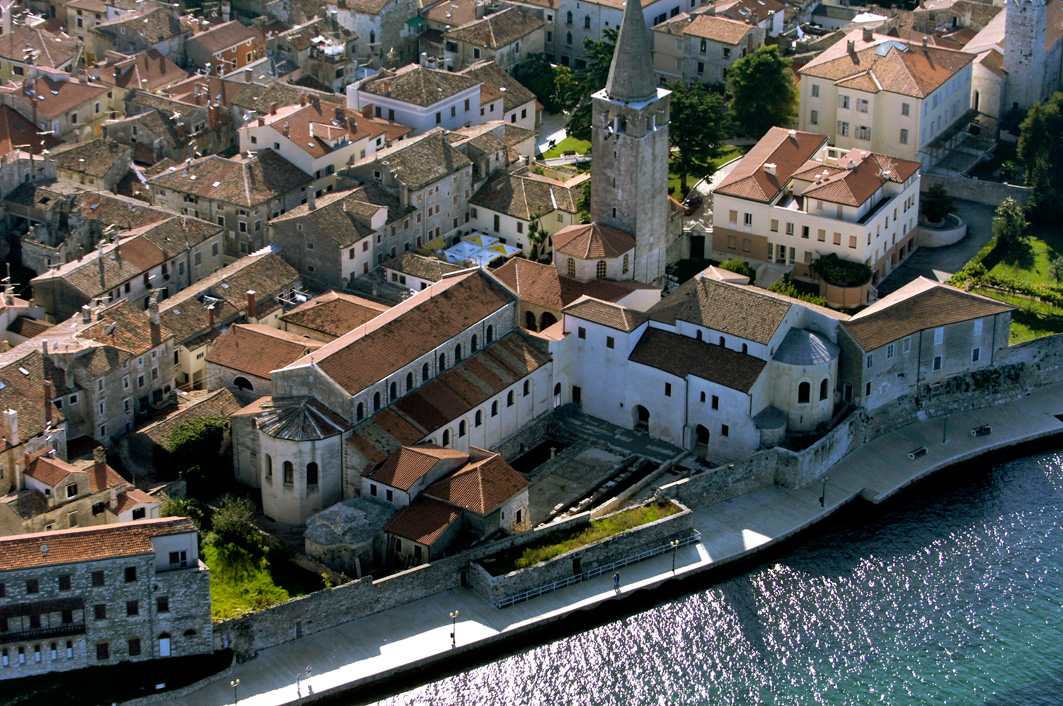
Poreč has a very long history and was initially the Roman town of Paretinum. The Euphrasian basilica is from the 6th century, and it remains one of the landmarks that makes Poreč recognisable to the world. It’s been on the UNESCO World Heritage List since back in 1997 based on its level of preservation and sheer beauty.

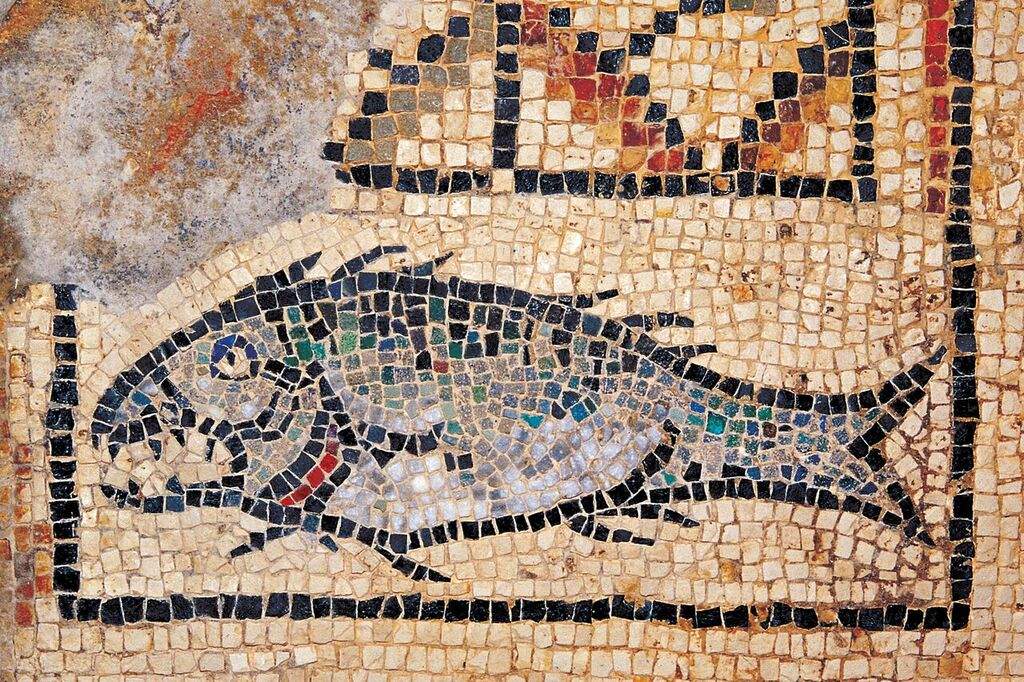
The history of Christianity in Poreč dates back to the 1st century after Christ (AD). At the end of the 2nd century, there was a Christian community under the bishop Mauro – they gathered secretly in his house which actually became the first church in the town. There lay a decorative fish mosaic which was an early Christian symbol.

The first bishop and clergy in Poreč all suffered martyrdom in the middle of the 3rd century, while in the year 313, the Christians were granted the freedom to worship in the Roman Empire. The former secret gathering place then became the very first public church.
At the same location, the first basilica was built during the second half of the 4th century, and that remains that of bishop Mauro and the other martyrs who moved to the early Christian cemetery. A larger basilica was constructed in the first half of the 5th century next to the existing basilica, and it was known as the Pre-Euphrasian basilica.
The floor mosaic of the temple area of the Pre-Euphrasian basilica was placed in the former sacristy. When Euphrasius first came to Poreč, he almost destroyed the old basilica in the mid-6th century, and built a magnificent three-nave basilica which still stands in Poreč today. At that time (543-554), the entire complex was made – the atrium, the bishops palace and the old baptistery.
The influence of Constantinople, the very centre of early Byzantine culture, is visible in the art and mosaics used in the construction and the decoration of the basilica. The floor of the basilica was covered with mosaics, and there were two layers of floor mosaics – the lower level belongs to the basilica from the fifth century, while the upper level is from the Euphrasian basilica of the sixth century.

The mosaics which decorated the interior are a valuable piece of heritage from the Byzantine era’s art, and thanks to the floor mosaic and its preserved inscriptions, we can witness all the periods of its building and restoration even in the modern day. The basilica was built on an already existing Roman heritage site, meaning that various Roman artefacts can be found there, too.
The first church had three parallel rooms, and the central one was used as a basilica and even then, it enjoyed the status of a cathedral. In the 5th century, there were two basilicas in the south which were placed in front of the current Euphrasian basilica, while in the north, the walls and columns were kept standing. There was also a baptistery which remained in use, followed by another which came later on.
To understand why the Euphrasisus wanted to build such a spectacular basilica, it is essential to understand the fact that in the 6th century, Poreč was a small town in the then dying Roman Empire, and the emperor Justinian wanted to restore the Roman Empire’s old glory. This is the time in which bishop Euphrasius started to build on the location of the ancient basilica and make this one of the biggest episcopal complexes of that time.
Shiny ”new” Byzantine art created a unique piece of heritage on the Roman foundation. When Euphrasius came to Poreč, he found a town boasting a very long history, and he became the head of the well established Christian community which already had a few martyrs like St Mauro and St Eleturis under its belt by then.
Euphrasius began construction on the foundation of the previous church where he found early Christian mosaics decorated with images of fish with the mosaic donators’ names inscribed on them, which helped in tracing the early Christian community in Poreč. There is one stone panel with an instruction written on it, from which we’ve been able to learn about the transfer of the body of St Mauro from a cemetery outside the town, to the place where the very first church originally once stood.

The new basilica, which was large in size, grew along with existing church objects. The construction of the basilica, the organisation of interior spaces, elements and ornaments, images on mosaics were all representing essential steps in the development of western art, influenced heavily by art from the east.
The entrance was formed one street before, and opposite the entrance, lies the baptistery – eight angles are from Pre-Euphrasian times, and the base is antiquity-era architecture. The structure of the wall and the wooden constructions of the roof are the work of local builders.

On the north-east angle of the basilica, there is a memorial chapel in which the layout is a bit different. The chapel, which was home to the relics of martyrs, has an oval atrium in front. The whole building underwent much needed restoration work in the 19th century.
The previous buildings on the site were construction material for the atrium, baptistery, and some parts of the basilica’s walls. The organisational structure of the complex is confirmation of the whole concept which bishop Euphrasius initially had in mind, and this highlights just revolutionary his ideas really were for that time period. The rich decorations of the interior are additional evidence of the advanced ideas Euphrasius had, and represented Byzantine influence.
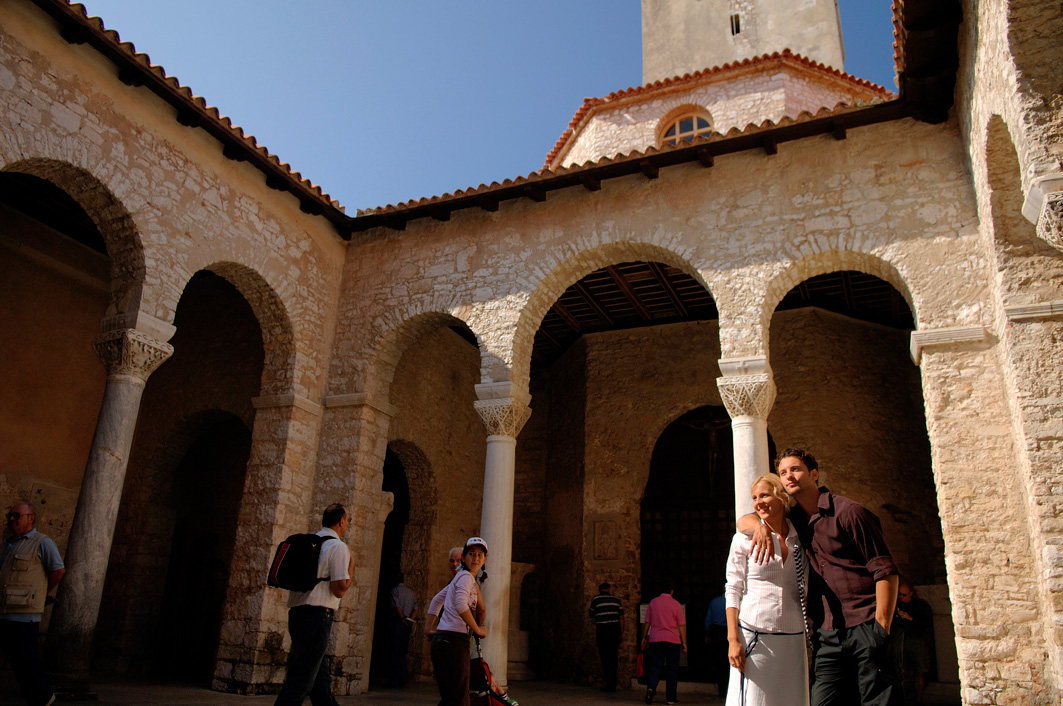
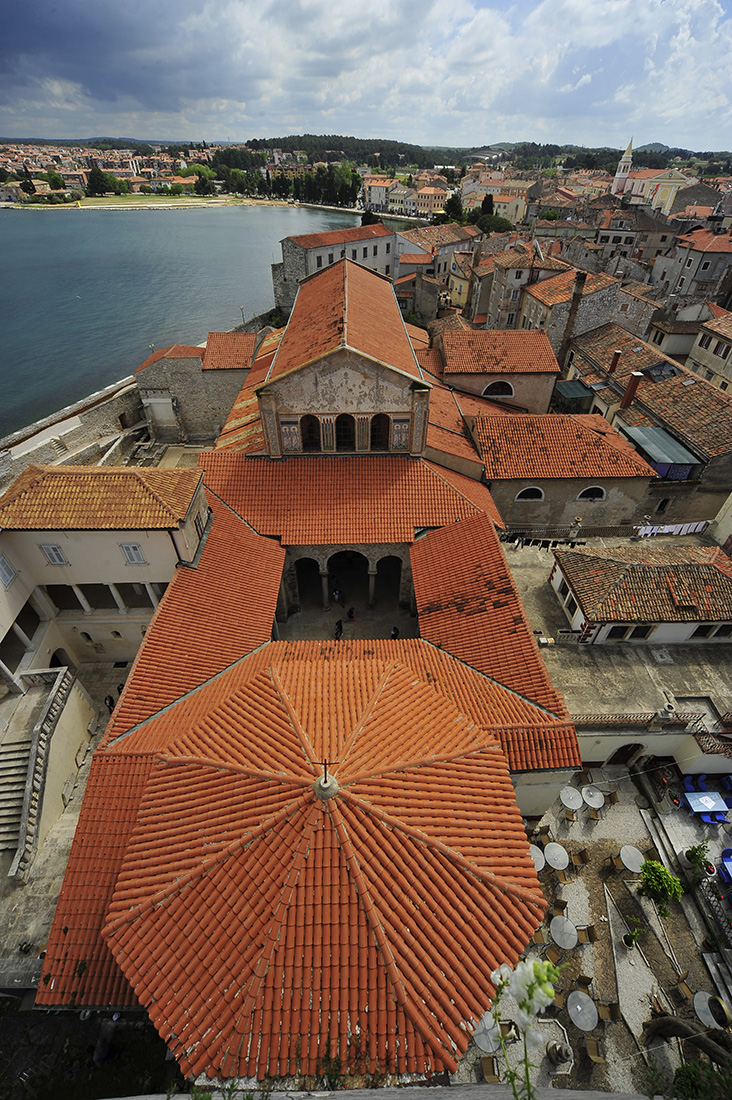
In front of the entrance to the basilica lies an atrium formed in the shape of a square, while the middle part of the atrium is an open space surrounded by arches – three arches on each side to be more specific. The eastern side of the atrium leads to the basilica and the western side to the baptistery. The central arch of these sides is elevated.
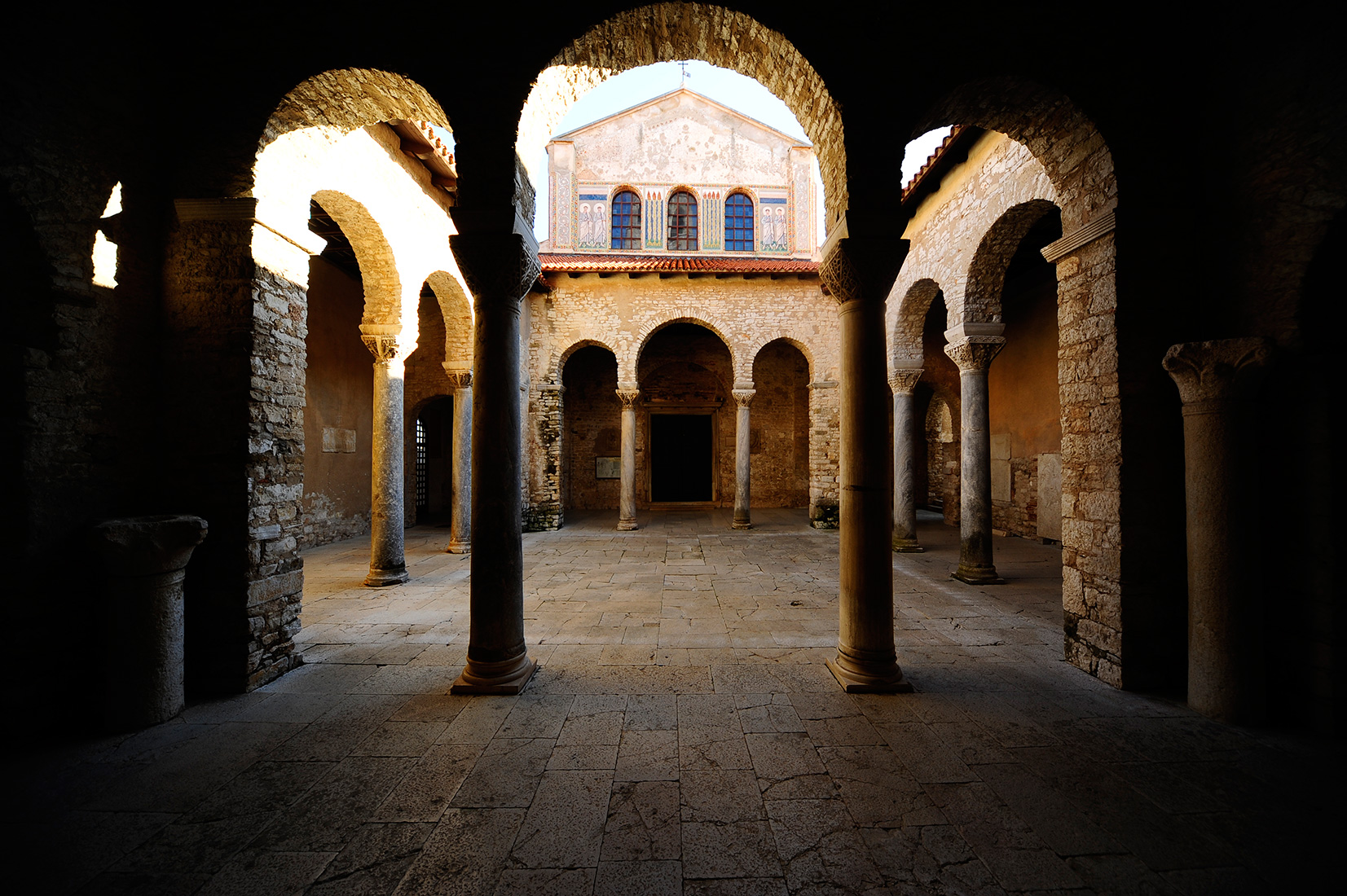

The arched-on columns and capitals were brought from Constantinople, just like with the one from the basilica. In the 16th and 17th centuries, during the great plague, the atrium and area around the church were used as a cemetery, with the atrium being rebuilt in the second half of the 19th century. Fragments of stone monuments from different periods of the Episcopal complex are displayed on its walls.
The baptistery is located in the western part of the Episcopal complex with the entrance facing the basilica. It was built in the 5th century and bishop Euphrasius had it restored and decorated in the 6th century. It was largely reconstructed in 1881 and then once again after the turn of the century, in 1935. The baptistery is an octagonal building with a hexagonal baptismal pool in the middle. It was surrounded with a sixteen-sided ambulatory, a sloping roof and three entrances.
The bell tower next to the Euphrasian basilica was built on the western side of the baptistery in 1522. Its 35 metres in height and provides a stunning view of the area. The bishops place is an integral part of the Episcopal complex, it is located in the northwestern part of the complex. On the first floor, there is a large ceremonial hall with a semi-circular apse on the northern side, it once used to be the audience hall, where the bishop received guests. Rights next to it on the left and the right sides there were once small chapels.

On the porch in front of the bishop’s palace lie some stone exhibits, capitals and various fragments of inscriptions in stone from previous basilicas in the area. The most important part of this lapidary is placed on the ground floor of the bishop’s palace. On the premises of the bishop’s palace, visitors can see different objects used by the church which span entire centuries.
The later built ciborium is part of the basilica from the 13th century, it presents as a masterpiece created seven centuries after Euphrasius’ initial work. In 1277, a large marble ciborium was made, and its canopy was set on four columns which were taken from the original ciborium. The new canopy was covered with mosaics and displayed an image of the Annunciation. From this time, visitors are able to see visible differences in the composition and design when it comes to iconography and images of the Virgin Mary and the angels.
In the 13th century, the process of cultivating various pieces of cultural heritage one after the other took place once again – older pieces of heritage was blended into newer pieces. Early Byzantine capitals and columns hold the construction of the new gothic canopy covered with mosaics which clearly mark the end of one era and the beginning of a new one, a process which slowly removed the characteristics of Byzantine art and shows the turn towards the Venetian influence.
The Venetian influence can be seen at the basilica by turning to western cultural influence – this is noticeable in all the future interventions and additional work on the basilica and in Poreč.
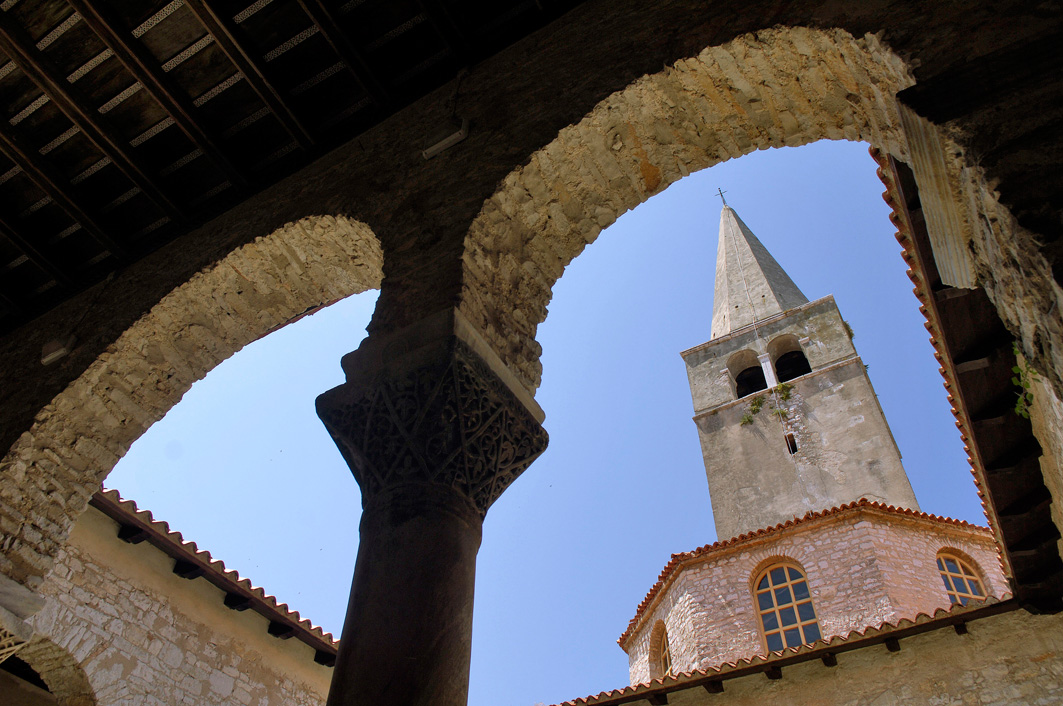

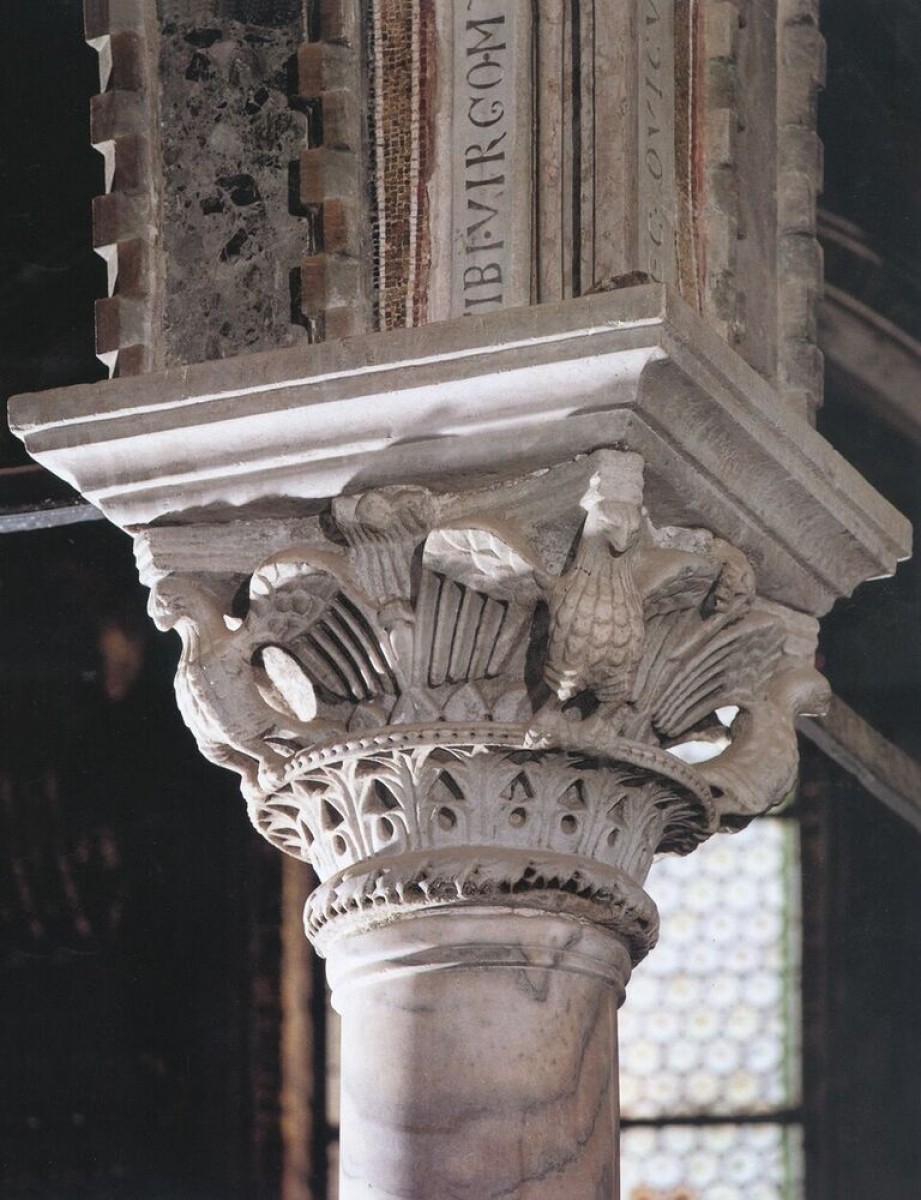
The naves of the basilica share two rows of nine arcades and are connected to their pillars on the wall at their western and eastern ends. The arcade consists of gray marble poles that are based on well-shaped bases, and in the upper part, they end with the capitals over which they are imposed on round medals, in which there are embellished Euphrasius monograms.
The basilica and the whole complex have various capitals, rich perforations, and ornaments. There are several marble panels decorated with reliefs with different symbols like crosses, monograms, birds, deer, stylised horns…

In the arcades on the north side, the stucco was also painted in its original form. This visual glitter should also add the incrustations in the lower part of the apse. The pieces of multi-coloured marble and nacre are placed on the walls and make for creative ornaments. In the apse, there are also marble seats for the priests who close the marble slabs with dolphin reliefs on the side, while the centre of the semicircle is the place for the bishop’s chair.
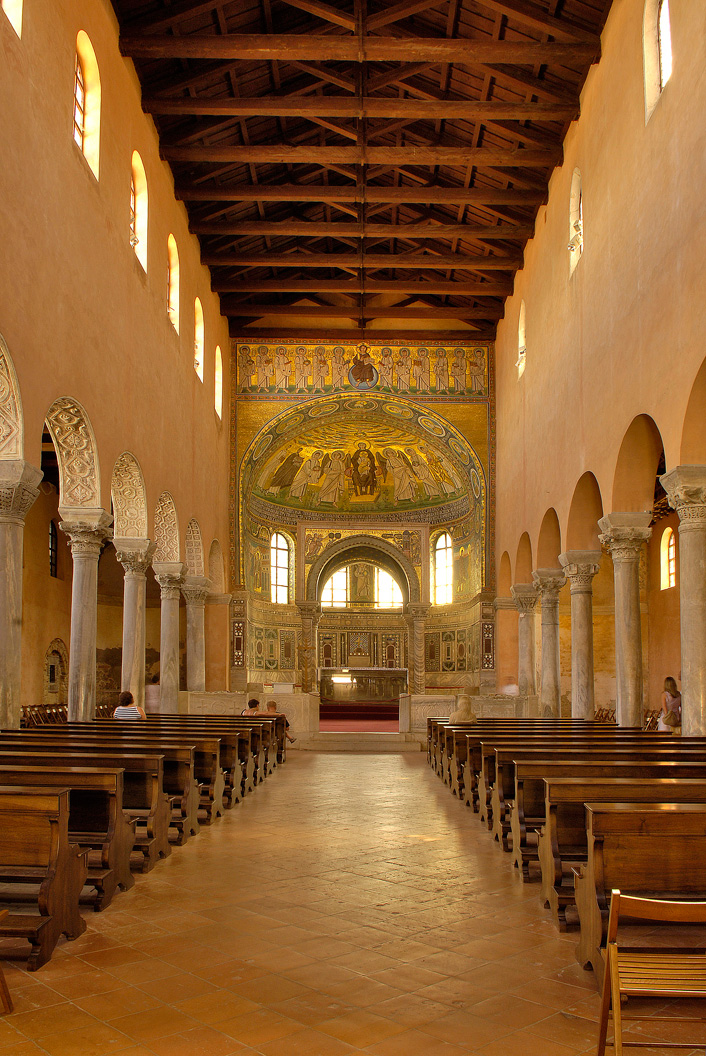
The walls of the Euphrasian basilica are one of the most valuable pieces of heritage as they boast various mosaics. Additionally, this is the place where iconographic innovation was applied for the very first time in the West. In the central part of the apse one can see the image of the Virgin Mary, which usually was the place for the image of Christ. The image shows the Virgin Mary sitting on the throne holding baby Jesus, who is wearing festive Roman clothes. On each side sit angels who are leading the groups coming to greet her. On the left side, three unnamed martyrs with wreaths in their hands and halos above their heads approach Mary, they appear like angels dressed in festive Roman clothes.
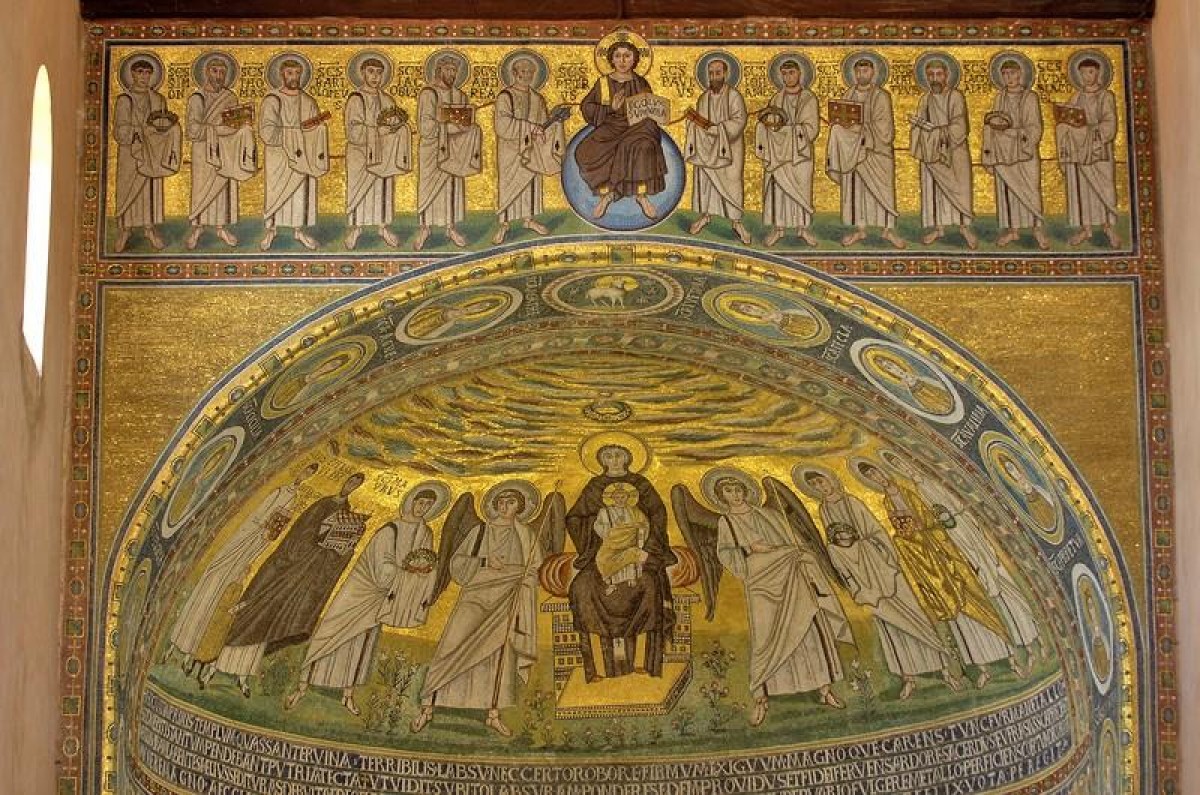

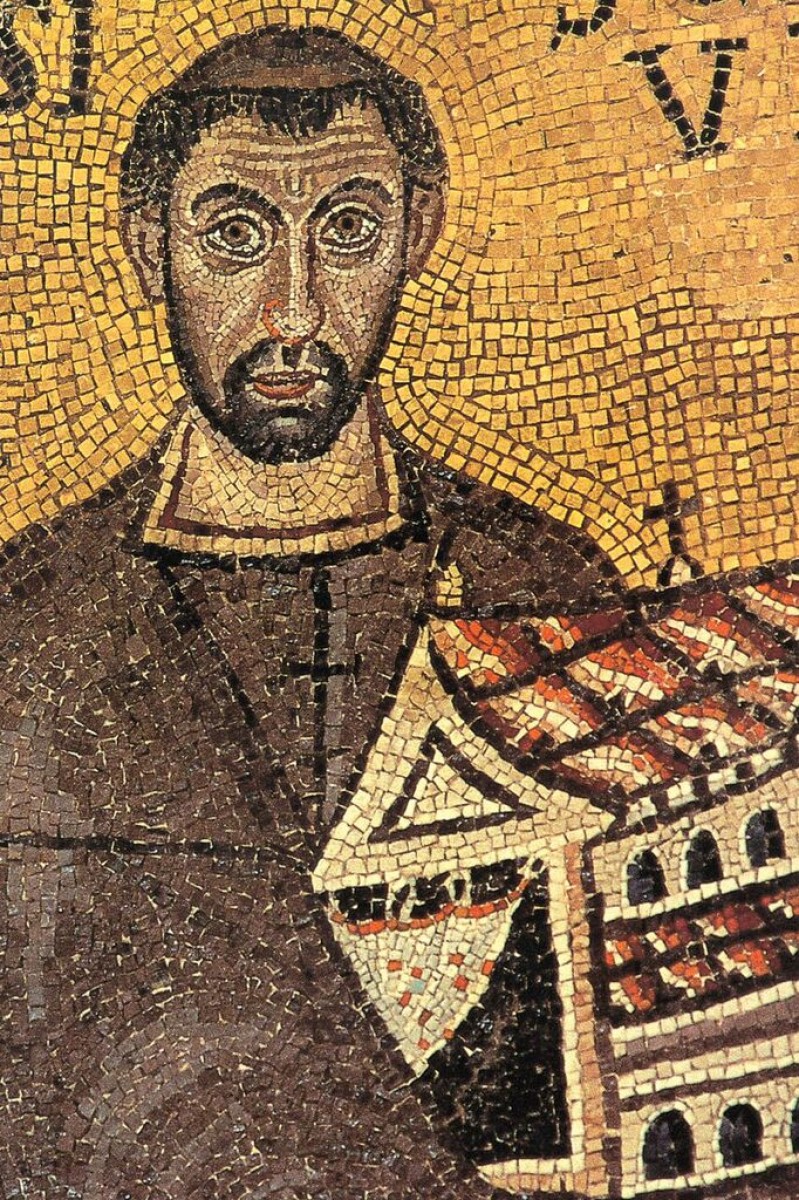
On the other side, behind the angel, stands St Mauro, depicted in the same way as the previous three martyrs, but with a printed name and a halo. This bishop and the saint of Poreč is leading a group of the contemporary people: the bishop Euphrasius holding the model of his basilica, the archdeacon Claudio (Euphrasius’ brother) and the archdeacons son named Euphrasius, as well. Euphrasius had written his desire to renew the old basilica there.
The angels and the holy martyrs of the parade surround the Virgin Mary on the throne. Opposite to them, the living characters without halos are depicted in an individualised manner, as if they were portraits.

Other mosaics depict a strong Christian iconography too. The image of the Virgin Mary is the central point of Euphrasius basilica. She is of course holding baby Jesus, and this image presents two of the unarguably central figures in Christianity. The image of Annunciation in Christian iconography is the connection between Jesus and Mary. The image of Annunciation is based on Luke’s gospel, and such images can be traced as far back as the 4th century in catacombs, while this iconography became more developed in the 5th century, as is visible in the Poreč basilica.
In the 6th century, in the time of Justinian and Byzantine-influenced art, the Virgin Mary wore the veil which symbolised her virginity. The Virgin Mary is pictured sitting on the throne whose columns blend with the basilica’s columns, which signifies the connection of the Virgin Mary to the church.
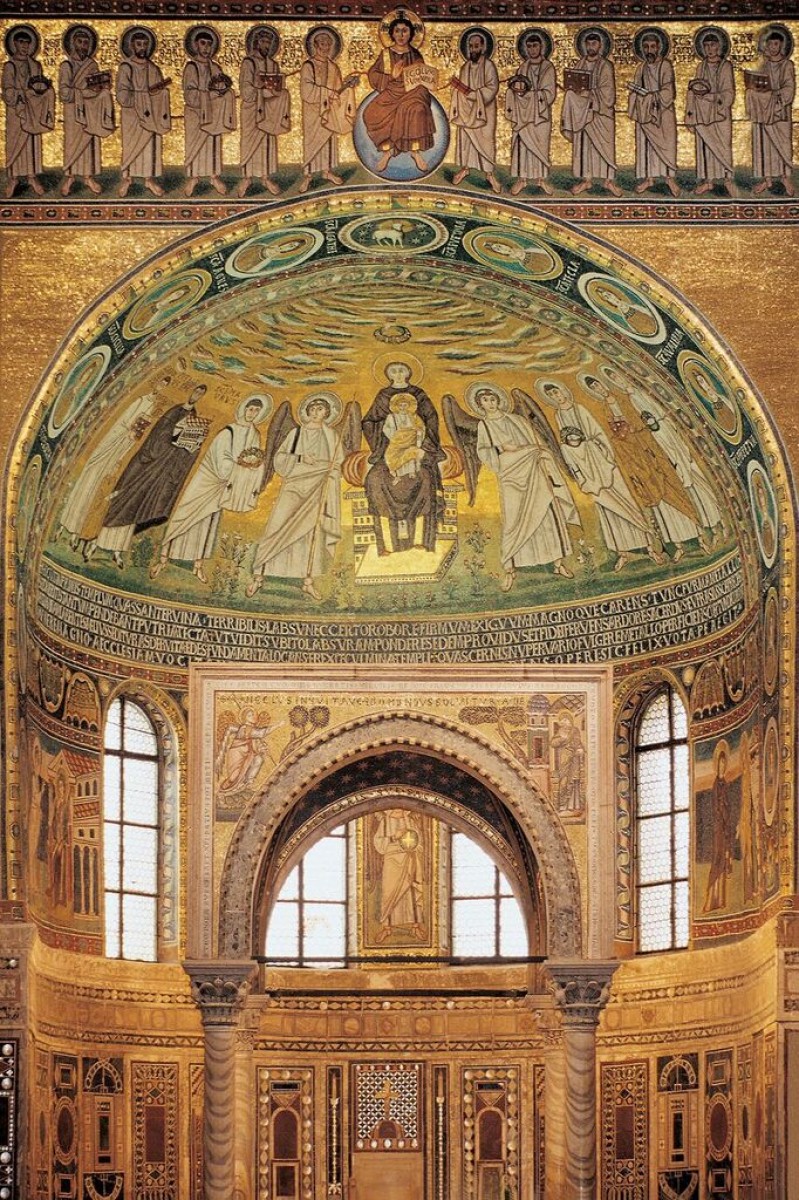

Mary holds a rove while an angel greets her. The angel is turned in a manner where half of its profile can be seen, which was specific for the art of the time, shown as if in movement, wearing bright clothes. Opposite to the image of the Annunciation sits the image of the visit of the Virgin Mary to her cousin Elizabeth. In the middle part of the apse between these two images from the Virgin Mary’s life, there is an image of Saint Zachary, an angel, and John the Baptist. In the lower part of the triumphal arch, there are thirteen round medallions.
In the middle section, there is the image of Christ shown as Agnus Dei, while on each side there are six saints pictured, along with their respective names. On the top part of the apse, there is an image of the apostles with Christ in the middle – Christ is presented as a young ruler who rules over the world. The Apostles are surrounding Christ in this image, and have their names written around their halos. In the higher parts of the side apse, there are fragments of mosaics boasting almost identical images – the large figure of Christ comes down from the clouds and is seen placing bay leaves on the heads of two martyrs.
Mosaics of the sort weren’t just placed in the interior of the basilica, but were placed on the outside too. Unfortunately, they weren’t preserved and were covered over when restoration work took place periodically. They originally showcased an image of Christ sitting on the globe, along with his Apostles.
With this extremely rich array of well preserved heritage, the Euphrasian Basilica is somewhere you must visit! Until you manage to pay it a visit, you can check out a virtual tour by clicking here (make sure you have Flash enabled!).

SOURCE(S) (text and photos): Tourist Board Poreč, Istra Culture, UNESCO