Let’s take a look into one of the best-known heritage sites in Croatia and the city that attracts millions of visitors each year. This in-depth article about Dubrovnik comes at about the same time as the 40th anniversary of the inscription of Dubrovnik’s old city on UNESCO’s World Heritage list, and the 10th anniversary of inscribing Festivity of St. Blaise onto UNESCO’s List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
Conveniently enough, we’re at the beginning of a very special month for Dubrovnik, for an event which has been happening each year on February the 3rd.
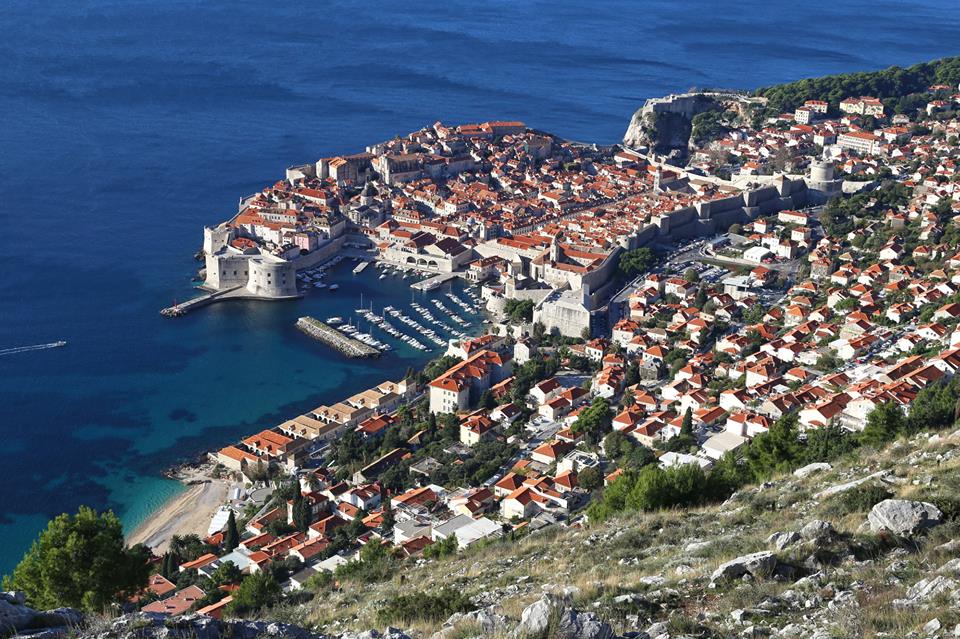
Well known as the ”Pearl of the Adriatic” or more recently as the popular Game of Thrones filming location (Kings Landing), Dubrovnik has been one of the historically most important Mediterranean ports since the thirteenth century. Dubrovnik has numerous preserved Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque churches, monasteries, palaces, and fountains. It did get damaged during the earthquake in 1667, and more recently during the Homeland War, but it still kept its beauty.

TZ Dubrovnik
To understand just why Dubrovnik has so much heritage and how it has been so well preserved, let’s take a look into this remarkable city’s very long history.
The Dubrovnik Republic, which represents the golden period of Dubrovnik’s history, perfectly regulated the city and life within it through its statute and other historic documents. This well-preserved city has been able to afford to lie on its Laurels owing to this, as well as its good geographic location and economy which was for centuries based on maritime and merchant activities.
The latest archaeological research discovered that there was a settlement dating back to the sixth century at this location, and this expanded with the arrival of Croats in the seventh century.
Travel and traffic between east and west during and after the Crusades resulted in the development of maritime and merchant centres in the Mediterranean and Adriatic in the twelfth and the thirteenth centuries. Another important event in the history of Dubrovnik was the Zadar Treaty, which in 1358 liberated Dubrovnik from Venetian rule while other Dalmatian towns fell under Venetian rule in 1420 and remained under their control up until the end of 18th century.
This is the reason why Dubrovnik was able to develop much more quickly than the other Dalmatian towns.

TZ Dubrovnik
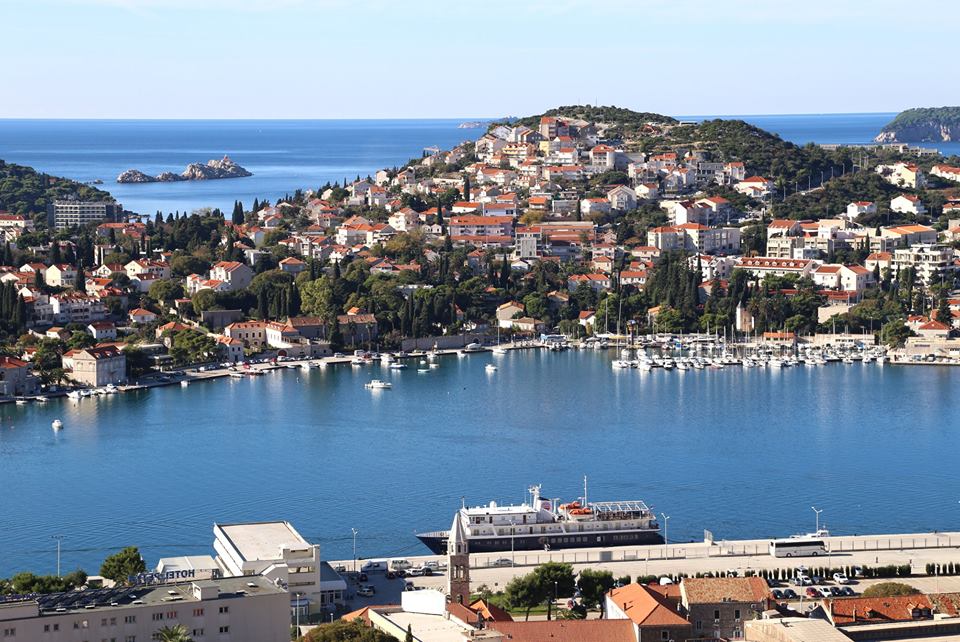
In the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, Dubrovnik was one of the most significant maritime and mercantile centres of Adriatic together with Venice and Ancona. Dubrovnik expanded its territory by using contracts and purchasing the land around the town including the islands, such as Mljet, Lastovo, the Elaphites, and of course Lokrum. The independence of the Dubrovnik Republic was completed by the fifteenth century when they had the independent election of the rector and council, and set their own currency, their own state flag with the image of St. Blaise, independent legislature and the right to establish consulates abroad.
The state authority was based on the great council which had members of aristocratic families in it. They appointed the members of the Senate and the small council which was the executive body of the great council. The rector was appointed on a monthly basis as a nominal symbol of authority.
In the fifteenth century, Dubrovnik had a well-organised transit trade route with the Balkan inland. In 1525, due to the Ottoman expansions in the area, the Dubrovnik Republic decided to pay tributes to the Ottomans and in return, they had the right to free trade throughout the growing Ottoman empire. The Dubrovnik Republic had no army on its own but managed to preserve its independence by being neutral in international conflicts and using the tutelage of powerful countries. The only rival of the Dubrovnik Republic was the envious Venetian republic.

TZ Dubrovnik
The Dubrovnik Republic’s golden age started in the sixteenth century – back then, Dubrovnik’s merchant navy matched those across the rest of the globe with its quality fleet of 180 to 200 ships. These ships were used for long and dangerous journeys through the Mediterranean and the Black sea, as well as ocean journeys to northern ports in England and Germany, even going as far as India and the Americas. Material prosperity helped to shape a humanist culture and the Republic received a great level of achievement in its urban and architectural development that has been maintained to the present day in its literature and poetry, sciences, and in many other fields of art and culture.
In the seventeenth century, the general crisis of the Mediterranean maritime affair also affected Dubrovnik’s maritime trade. The catastrophic earthquake in 1667 was another awful event for the Dubrovnik Republic. In the eighteenth century, Dubrovnik got another chance at the economic revival of maritime trade under a neutral flag. In 1815, Dubrovnik joined other parts of Dalmatia and Croatia. In more recent history, Dubrovnik was damaged during the Homeland War, with the worst attack happening on December the 6th, 1991.
Now, let’s see what can be found in Dubrovnik when it comes to valuable heritage which has been recognised by UNESCO and numerous people who visit Dubrovnik each year.
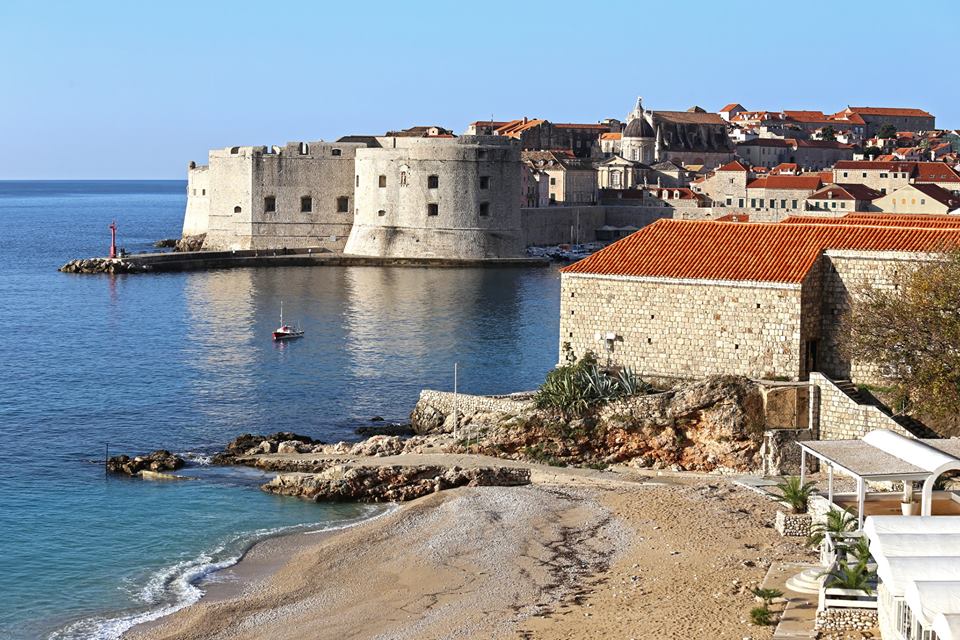
Dubrovnik’s City Walls

TZ Dubrovnik
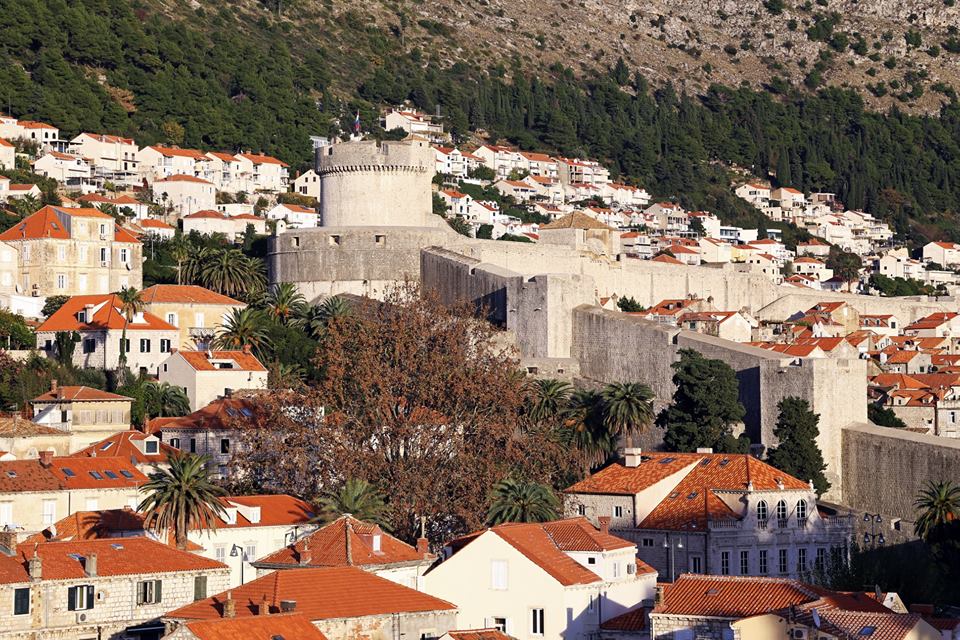
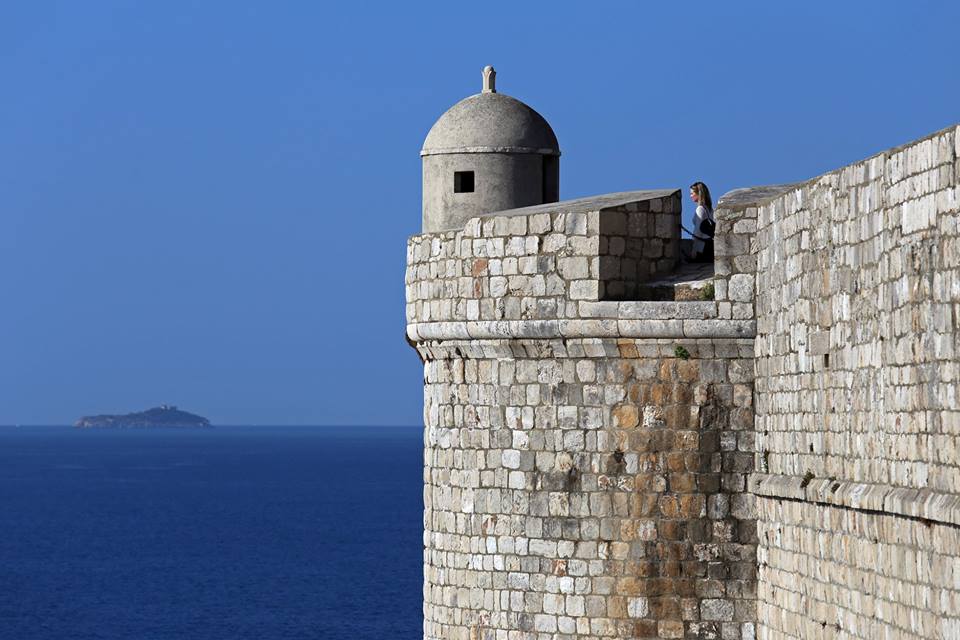
Dubrovnik’s city walls were established in the thirteenth century and were systematically and continuously perfected over several hundred years, until 1660, when the last tower, the St. Stephen’s Bastion, was finished. The walls stretch for over 1940 metres and consist of the main wall, sixteen towers, three forts, six bastions (bulwarks), two corner forts (cantonatas), three pre-walls with several turrets, three moats, two barbicans, two drawbridges, and one breakwater.
This is one of the best-preserved fortification systems in Europe with three forts: Minčeta, Bokar and St. John. The walls are up to 22 meters high in some places, with a thickness of between 4 to 6 meters from the mainland side, and from 1/5 to 3 metres on the seaside.
Among the many known and unknown builders of the wall and its construction, some of them are: Paskoje Miličević, Nicifor Ranjina, Marin Držić, Župan Bunić, Miho Hranjac, Juraj Dalmatinac, Michelozzo di Bartolomeo Michelozzi of Florence, Onofrio and Simeone Della Cava, Antonio Ferramolino of Bergamo, Giovanni da Siena, Bernardino di Parma, Marcantonio Bettaci of Florence, Seporoso Mateucci of Fermo and Giovanni Baptista Zanchi of Pesaro.
The shape of the walls was definitely defined by available weapons of the time and the various defence techniques of the past. The first walls were built when the first settlement was consctructed back in the eighth century, and Dubrovnik enjoyed the natural protection of the sea, with the walls acting as additional protection for Dubrovnik’s citizens.
You can enter Dubrovnik’s city walls next to Pile Gate, St. John’s Fort and St. Luke’s Fort.
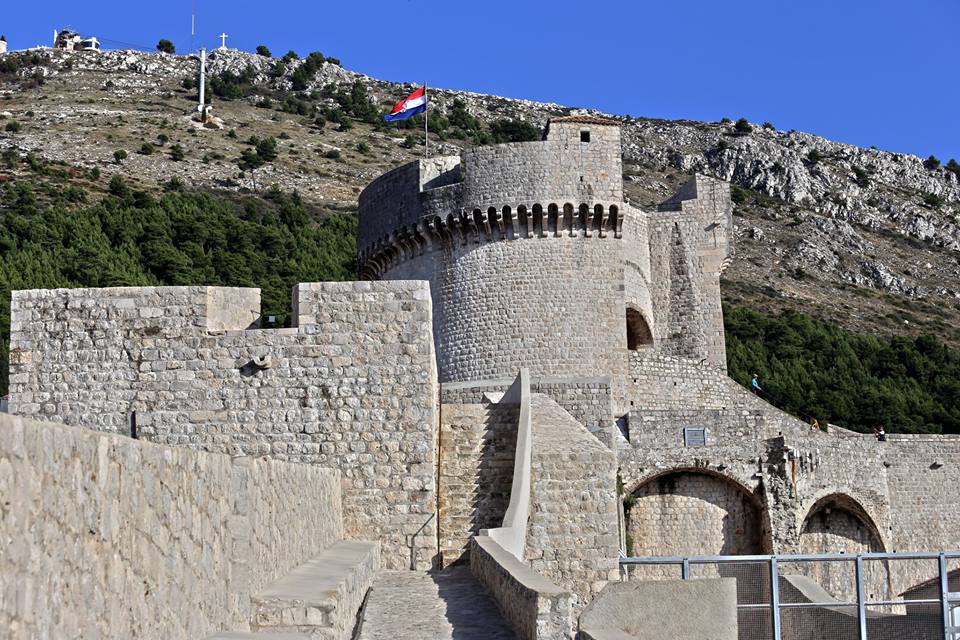
Minčeta Fortress

TZ Dubrovnik
Minčeta fortress is placed on the highest north-western part of the city. It is a large circular tower with a big battlement suspended by a stone support. The first quadrangular tower was constructed by Nikifor Ranjina in 1319, the architect Michelozzo Michelozzi gave it its present form and it was completed in 1464 based on the design of Juraj Dalmatinac, who was famous for numerous works in Dalmatia among which the best-known is the Šibenik cathedral, another UNESCO world heritage site.
St Luke’s Tower

TZ Dubrovnik
If you walk eastward along the city walls towards Ploče gate, you will get to St. Luke’s tower. In 1467. Paskoje Miličević designed the bulwark for the old St. Luke’s tower with openings for cannons. The tower controlled the access to the harbour.
St John’s Fort

TZ Dubrovnik
This is the first quadrangular pier tower and it was constructed back in 1346 in order to protect the city harbour in the southeast, and its outlines are still visible on the western wall. The shape of the fort we know today was completed in the sixteenth century when the whole complex got bigger and outer wall was extended.
Bokar Fort

TZ Dubrovnik
This fort was important for defending the city. The gate and the bridge, as well as the moat are located at Pile. The semi-circular tower was designed by Florentine architect Michelozzi in the fifteenth century.
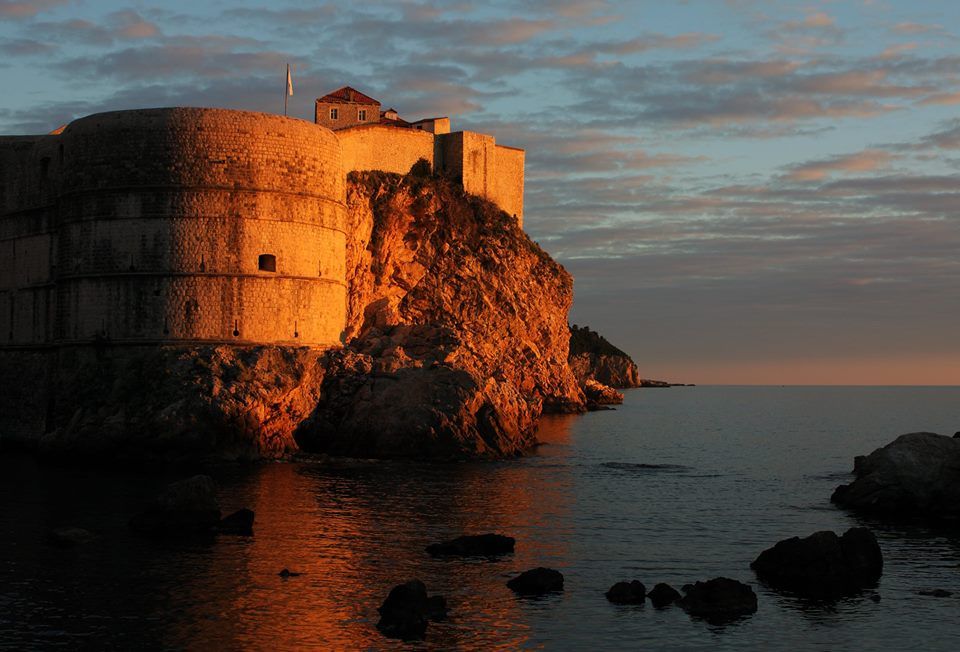
Lovrijenac
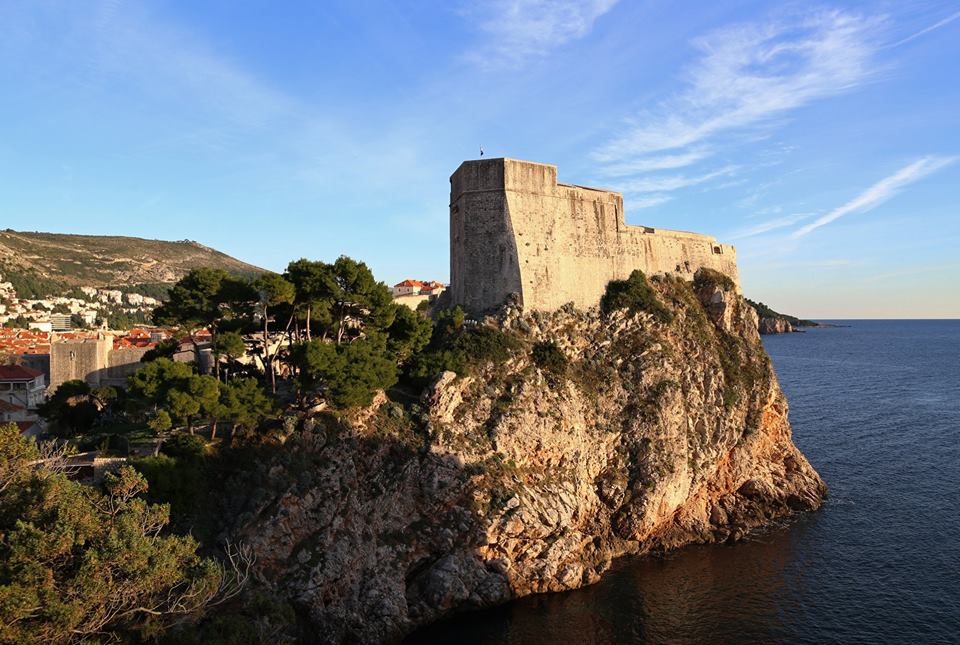

TZ Dubrovnik
This fort is set on the 37-metre-high cliffs outside of the city walls. You can reach it by walking along Pile bay and climbing the steep, stone stairs. This fort was built to protect the entrance to the city from the west. The fort’s construction began in 1018 and it was completed in the sixteenth century. The walls are 4 to 12 metres thick. The entrance door boasts the Latin inscription: Non bene pro toto libertas venditur auro (Freedom is not sold for all the gold in the world). There lies the chapel of St. Lawrence and its courtyard where occasional performances and plays are held today.
Revelin Fort
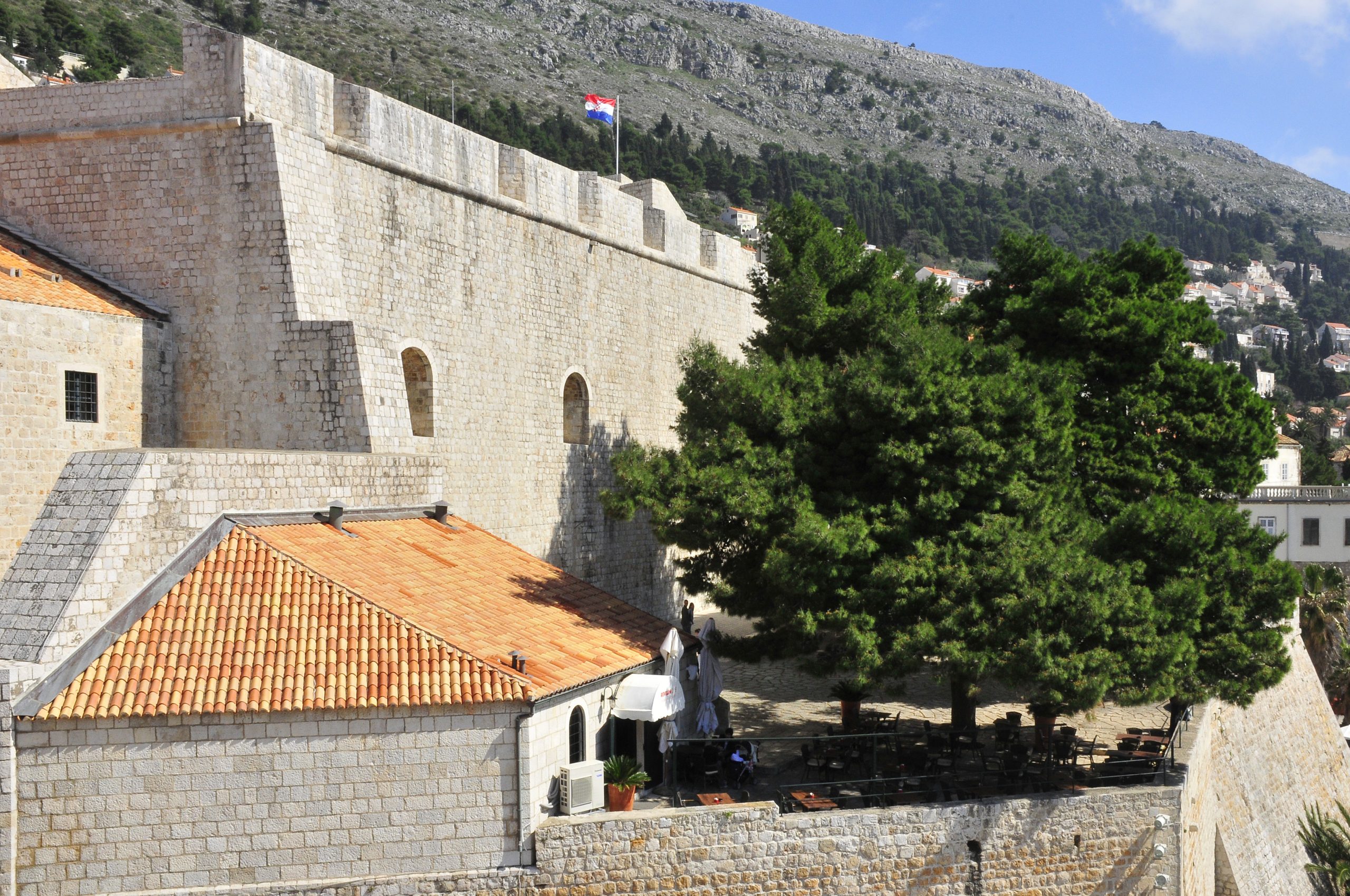

LBM1948
Revelin fort was built outside of the city walls and it was once part of the defence complex of Ploče Gate. The lower part of the fort was built in 1463, and was then rebuilt in 1538. The fort protected the eastern part of the city and the entrance to the city harbour. It has three entrances and is surrounded by a moat and the sea on three sides. Ivan Rabljanin kept the foundries for casting cannons and bells in the large interior. Now it is used as a place for Dubrovnik summer festival plays.
Pile Gate
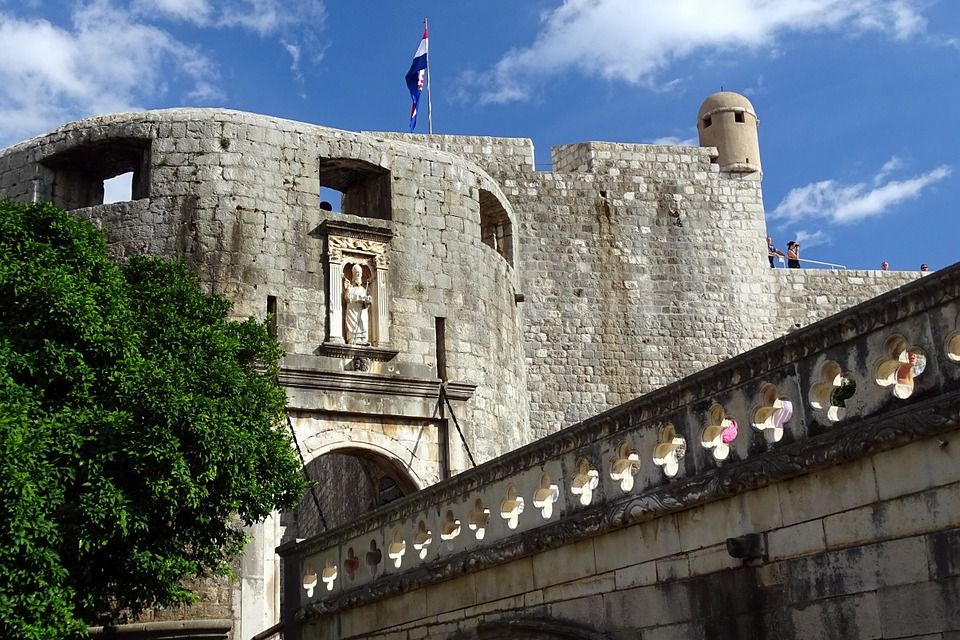

Pixabay
Just outside the city walls lies Pile – here, you first have the seaside promenade constructed outside of the walls. Here you enjoy an amazing view of the city walls and of Lovrijenac fort. If you enter the city through Pile Gate, the first thing you will see is the stone statue of St. Blaise. There is a stone bridge and a wooden bridge which lead to the outer gate, then to the renaissance semi-circular tower. When you pass through the inner gate, you enter Dubrovnik’s main street – Placa or Stradun.
Stradun
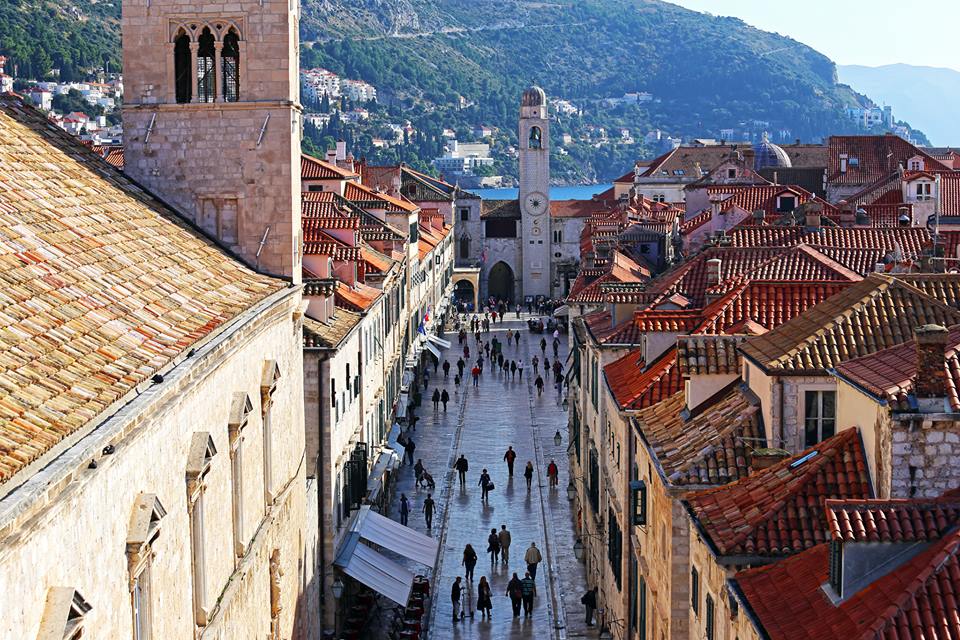

TZ Dubrovnik
Placa or Stradun is the main street in Dubrovnik. Stradun is 298 metres long and the statute of the city from 1272 determined the final plan for the city and its main street. The houses on Stradun are built in baroque-style architecture with shops on the street level. Stradun has its modern-day shape after the earthquake in 1667, when a large number of gothic and renaissance palaces were sadly destroyed. Even today, Stradun is the main centre for all the events in the town.
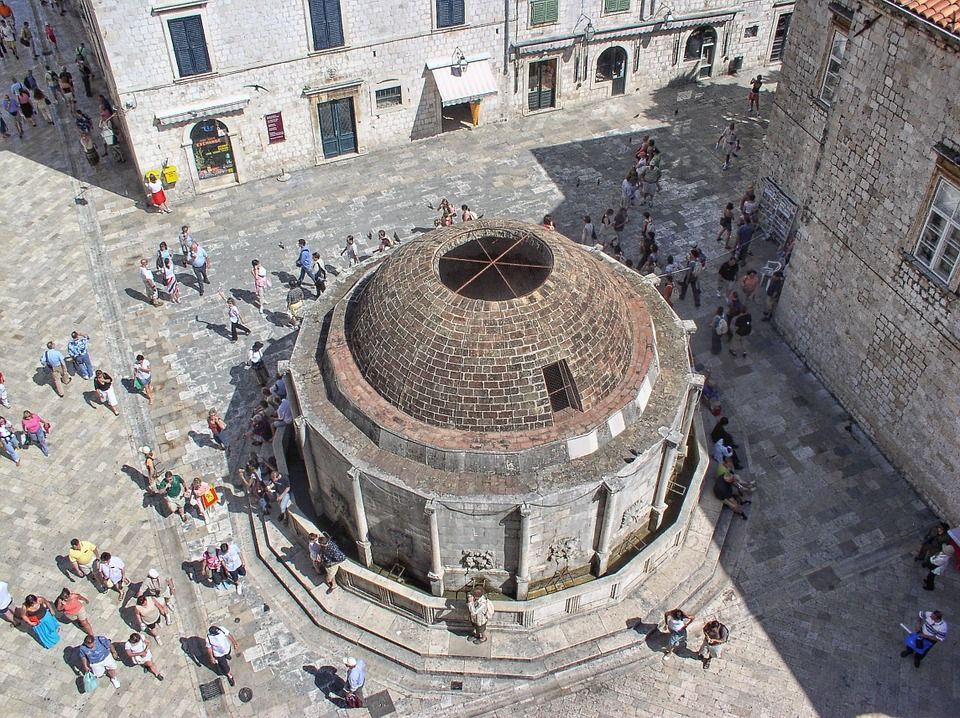
Large Onofrio’s Fountain

Pixabay
When on Stradun, one of the main sights is the large Onofrio’s fountain. This is a large polygonal fountain with sixteen stone carved maskerons which provide running water. The fountain was designed by Onofrio Della Cava who also designed the small fountain at the other end of Stradun – the fountains were built for public use in 1438 when fresh water was brought to the city from Rijeka Dubrovačka. The fountain is now connected to the new waterworks system. The cupola was damaged during the 1667 earthquake and later reconstructions sadly failed to restore it.
Small Onofrio’s Fountain
Sailko
Small Onofrio’s fountain was designed in 1446 and the stone mason work was handled by Pietro di Martino di Milan. Located in a niche to the city guard building, it is part of the original setting for the carnival play “The tale of Stanac” by the famous Dubrovnik playwriter Marin Držić.
City Guard Building

Pixabay
The City Guard building was the admiral’s residence during the fifteeth century. It was restored in the twentieth century and it is now the entrance to the cinema.
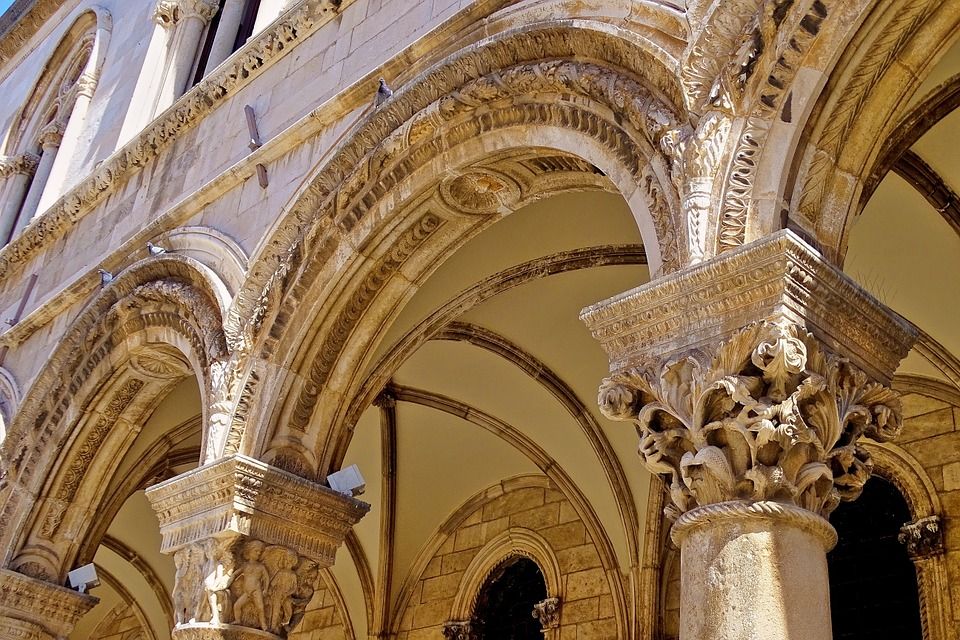
Rector’s Palace

Pixabay
The Rector’s Palace is one of the most important pieces of heritage on the Croatian coast – this was the administrative centre of the Dubrovnik Republic – it is built in a gothic style with reconstructions in renaissance and baroque style. It was damaged in the fifteenth century by gunpowder explosions and restored by Onofrio Della Cava in late gothic style in 1435. The second gunpowder explosion in 1463 destroyed the western facade
and the two famous architects Juraj Dalmatinac and Michelozzo worked on reconstruction. After the earthquake, the atrium was partially reconstructed with a baroque staircase. During his one month mandate, the rector lived in the palace which was the place of both the minor and major council hall, the rector’s residence, the city’s courtroom, the administration office(s), the prison, and even for arsenal and gunpowder storage.
Above the entrance door lies the inscription: Obliti privatoru publica curate (Forget your private business, concern yourselves with public affairs).
In the atrium sits the bust of a rich sea captain and benefactor, Miho Pracat, this work was done by P. Giacommetti in 1628. The Miho Pracat statue is the only statue in the city for the common people – The former Dubrovnik Senate decided to do this 1638. The bust is placed between two columns in the eastern wing of the Rector’s palace atrium. He was not only a rich seaman who left his wealth to the Republic, but a ship owner and a very skilled merchant. This was an enormous honour as the Dubrovnik Republic never built statues for its contemporaries, and found it inappropriate to have statues in public places. Today, the Rector’s Palace is the home of the Dubrovnik museum.
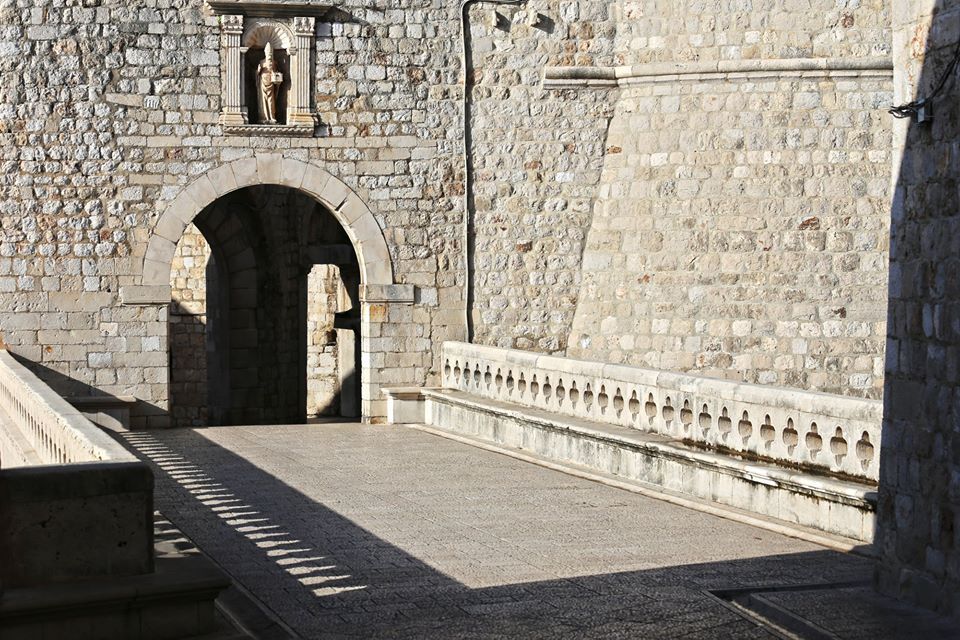
Ploče Gate

TZ Dubrovnik
Ploče gate is the eastern entrance to the city. When you pass through this gate, you will see two small churches. This entrance is fortified and had inner and outer gates with stone bridges from the fifteenth century onwards, and there lies a statue of St. Blaise, the city’s patron saint.
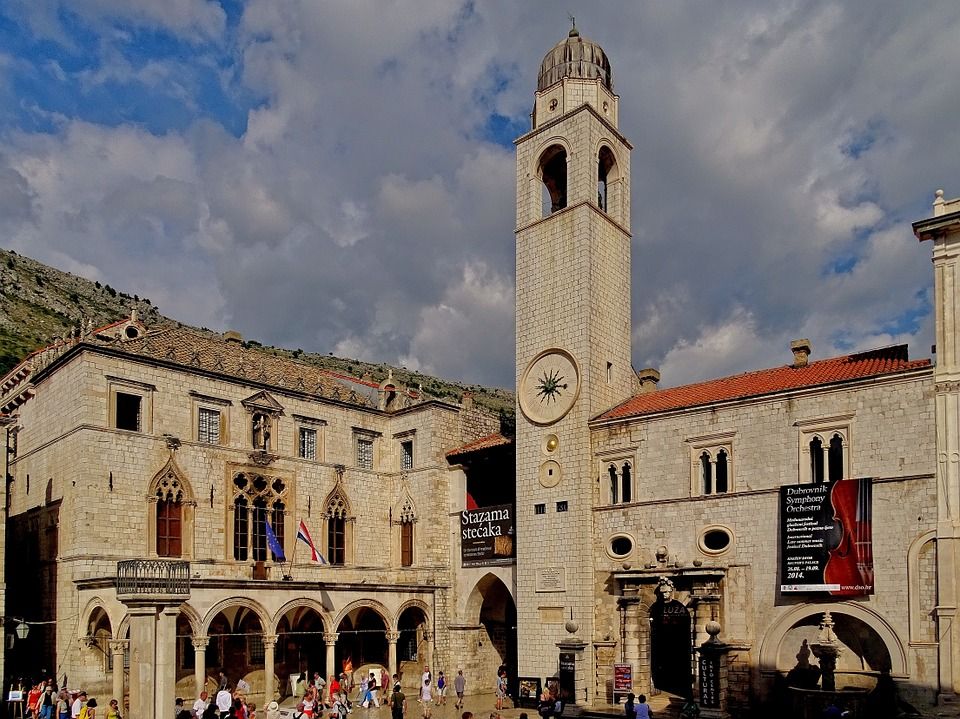
Luža and the City Bell Tower
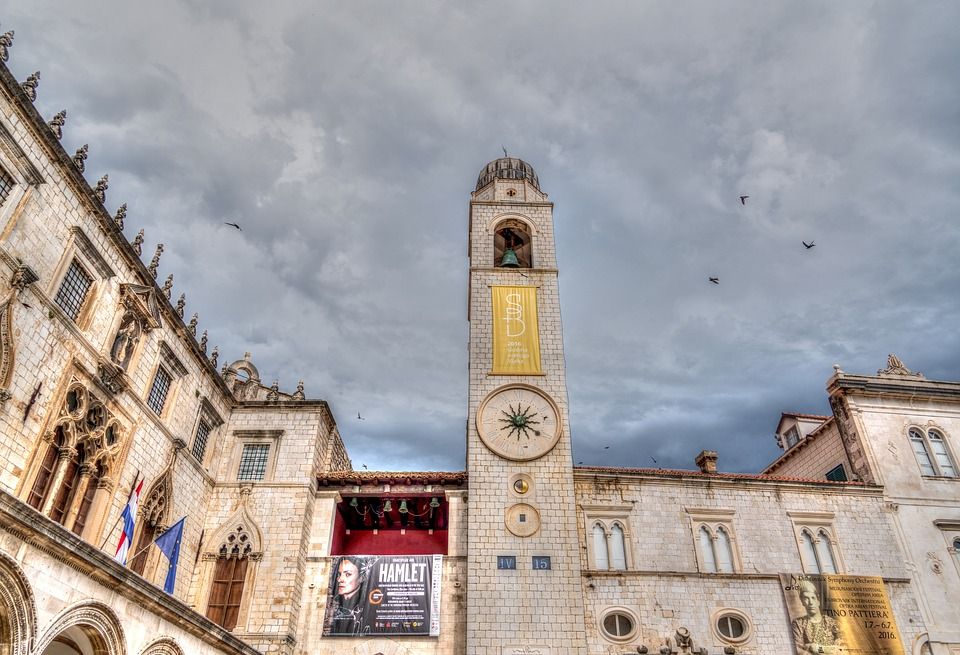

Pixabay
After passing through Ploče gate, you will end up in front of Luža and the City Bell Tower. The bell tower, built in 1444, once had figures called Zelenci who struck each hour with their hammer. The bell tower was damaged in the earthquake and it was rebuilt in 1929, while the Zelenci figures were replaced with replicas.
Sponza Palace
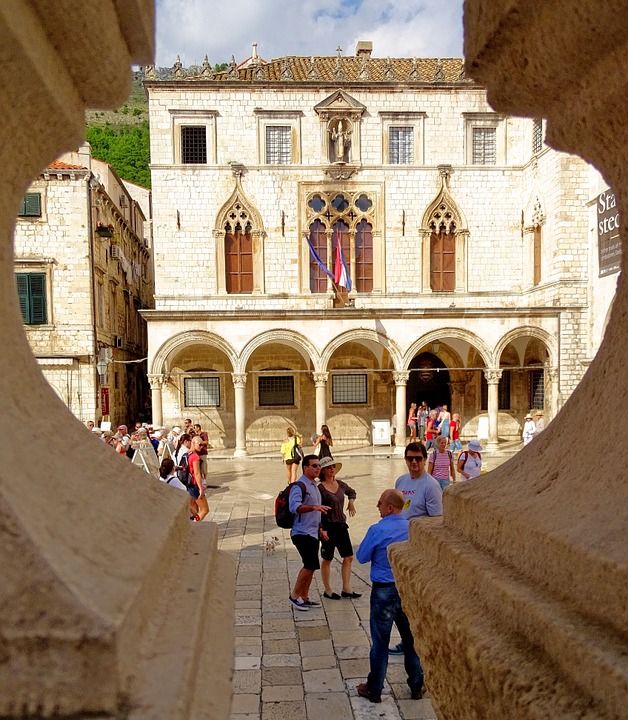

Pixabay
Right next to the bell tower lies Sponza Palace. This building is the best example of Dubrovnik’s highly specific gothic-renaissance style. It was constructed in the sixteenth century based on the design of Paskoje Miličević. It was built in a rectangular shape and has a portico and an atrium. On the main wall lies the inscription: Fallere nostravetant, et fall pondere, meqve pondero cvm merces ponderat ipse deus (We are forbidden to cheat or falsify measures and when I weigh goods, God himself is weighing them with me).
This was the liveliest commercial centre of the city and in the seventeenth century, it became the meeting point for members of the Academy who discussed literature, the arts, and science. Today, it’s the home of the Dubrovnik archives.
Church of St Blaise
TZ Dubrovnik
The Church of St. Blaise is one of the most important buildings in Dubrovnik. St. Blaise is the patron saint of Dubrovnik who has been celebrated every year on February the 3rd, and this festivity is part of the city’s UNESCO intangible heritage. The church got its present form is from 1715 and is a shining example of Venetian Baroque. It was built by Marino Gropelli upon the request of the Dubrovnik Senate. It was damaged in the earthquake, and then again in the fire in 1706.
In that fire, everything was destroyed except the silver statue of St. Blaise. This statue was then kept in the small church of St Nicholas on Prijeko before being brought back to its original place in 1715. This statue is one of the most valuable sculptures in Dubrovnik and the saint holds the city model, from which one can see how Dubrovnik once looked long ago. St Blaise has been being celebrated in Dubrovnik from the tenth century onwards, when he saved the people of Dubrovnik from a surprise Venetian attack with a solemn warning.
Orlando’s Column
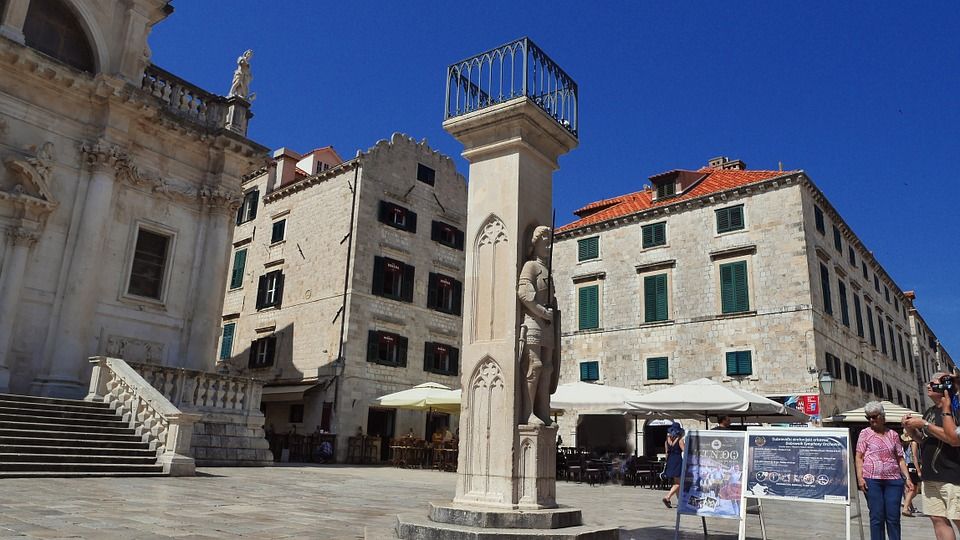

Pixabay
In front of the Church of St. Blaise lies the most important symbol of statehood and freedom for Dubrovnik – Orlando’s column. Orlando’s column was constructed by Bonino di Jakopo and Antun Raguso. Erected in 1419, Orlando’s column, with the statue of a medieval knight, stands in the square and presents Roland, the eighth-century knight from the Chanson de Roland. The reason this statue is in Dubrovnik is probably because it was brought by King Sigismund, a Hungarian and Bohemian king who was the patron of Dubrovnik Republic.
Additionally, there is a legend that says Roland saved Dubrovnik from Saracens and defeated them near the island of Lokrum. Senate decisions were announced in front of it. This statue was also a punishment spot and a pillar of shame. The white flag of the Dubrovnik Republic with the image of St. Blaise remained on the column until the abolition of the Republic in 1808. Now the Croatian flag flies there, and the flag is changed only during the Festivity of St. Blaise and during the Dubrovnik summer festival. This year, Dubrovnik is marking the 600th anniversary of the construction of Orlando’s column, and therefore 2019 is considered to be the year of Orlando.
Buža Gate
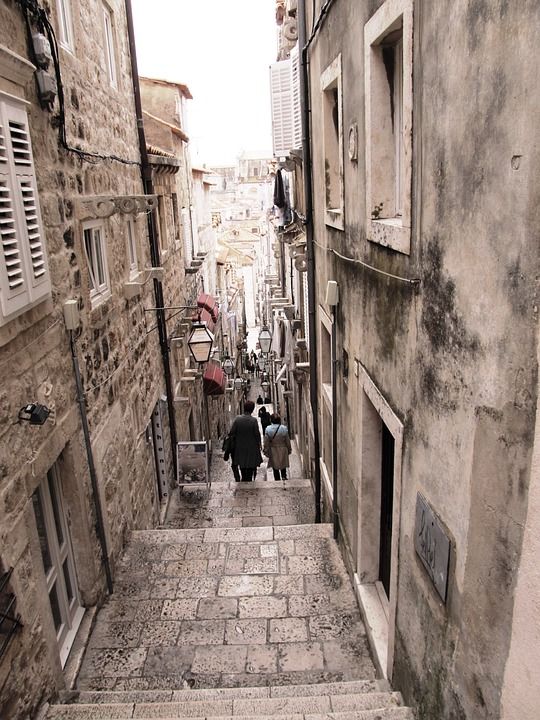

From Prijeko to Ruđer Bošković street (the place where the famed eighteenth century Croatian scientist, physicist, astronomer, and poet was born) stands the gate that was built back in 1907.
Gundulić Square
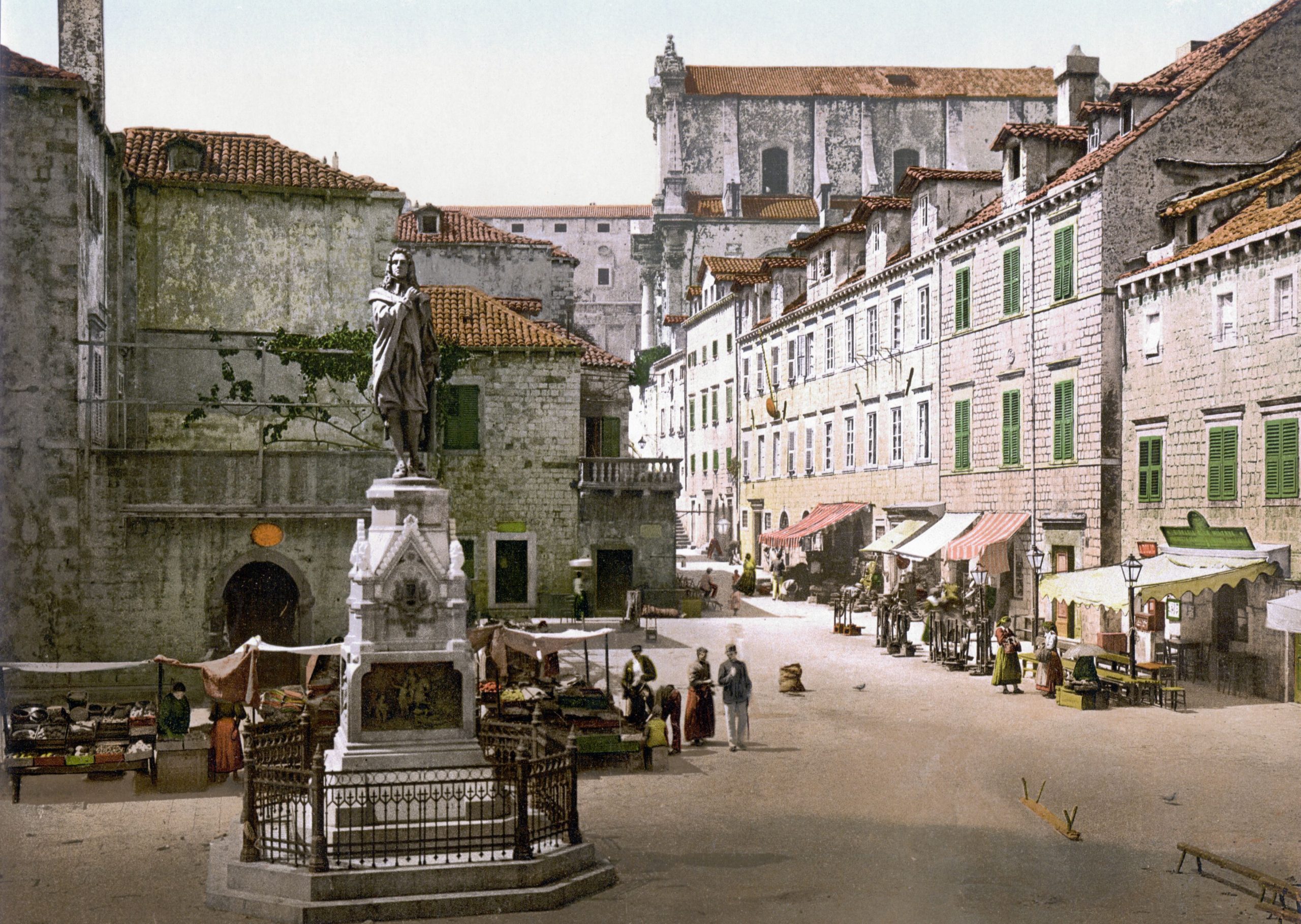

Behind the cathedral lies Gundulić square which is home to the statue of Ivan Gundulić, one of Dubrovnik’s best eighteenth-century poets – this statue is the work of Ivan Rendić, and on the base of the statue there are bronze relives with scenes from Gundulić’s epic poem – Osman. Ivan Gundulić was born in 1589 to an old and respectable aristocrat family. He later became famous on his own merit for his valuable works. This is the place where the green market in the morning sets up. What is interesting is that in front of the statue there are hundreds of pigeons waiting for their meal every single day – the city funds ten kilos of corn to feed the pigeons.
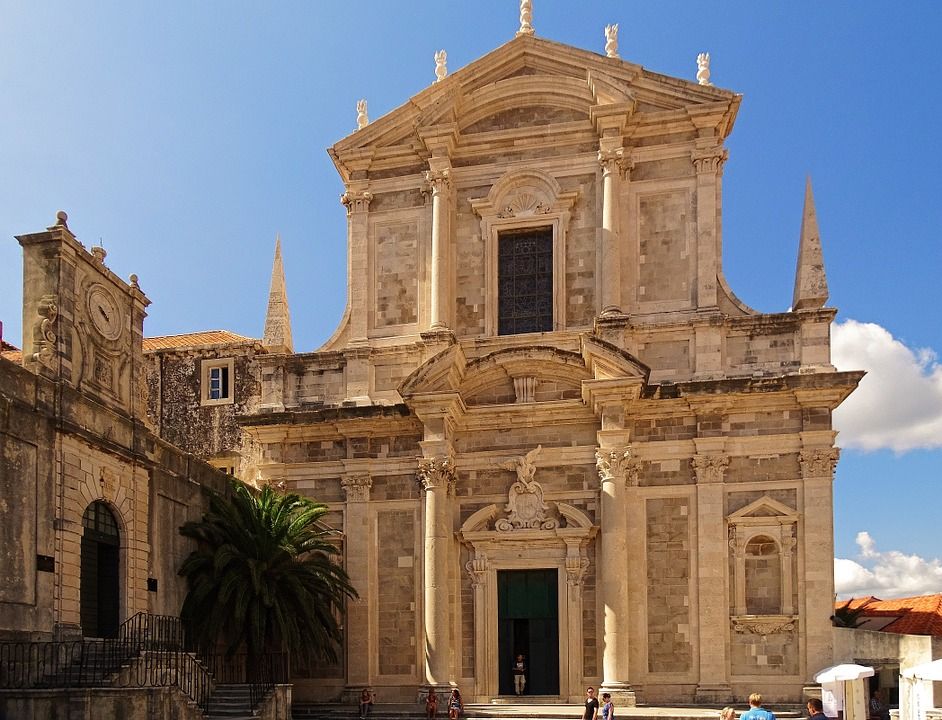
Jesuit Church

Pixabay
From there, if you go up the baroque stairs you will reach the Church of St. Ignatius or Jesuit church which is the home of Dubrovnik’s most beautiful baroque complex. This church is the work of Ignazio Pozzo and right next to it is Collegium Ragusinum, the famous Jesuit school. Collegium Ragusinum was initially founded because the people of Dubrovnik were dissatisfied with their Italian teachers. The first steps for this to happen were initiated in the sixteenth century but it wasn’t until the end of seventeenth and the beginning of the eighteenth century that works started. Collegium Ragusinum hosts a massive 10,000 volumes with incunabula and manuscripts by Dubrovnik’s numerous writers.
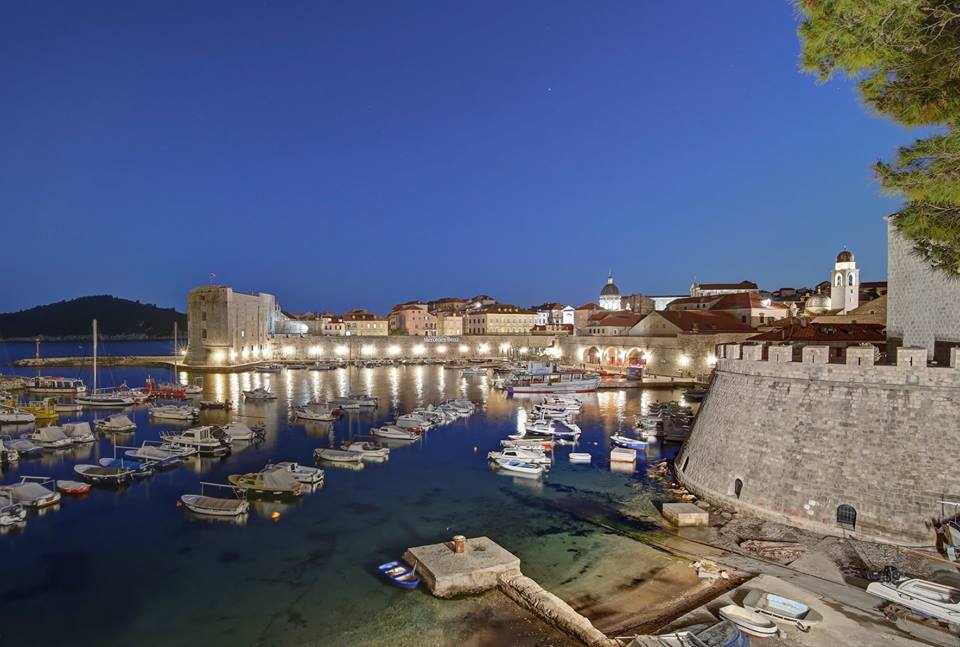
City Harbour

TZ Dubrovnik
The city harbour got its look back in the fifteenth century – the most recognisable part of it is the three arches of the large arsenal. East from the large arsenal there is the fish market gate and then three arches of small
arsenals where smaller ships were repaired. At the location of the large arsenal today lie the city cafe and the theatre.
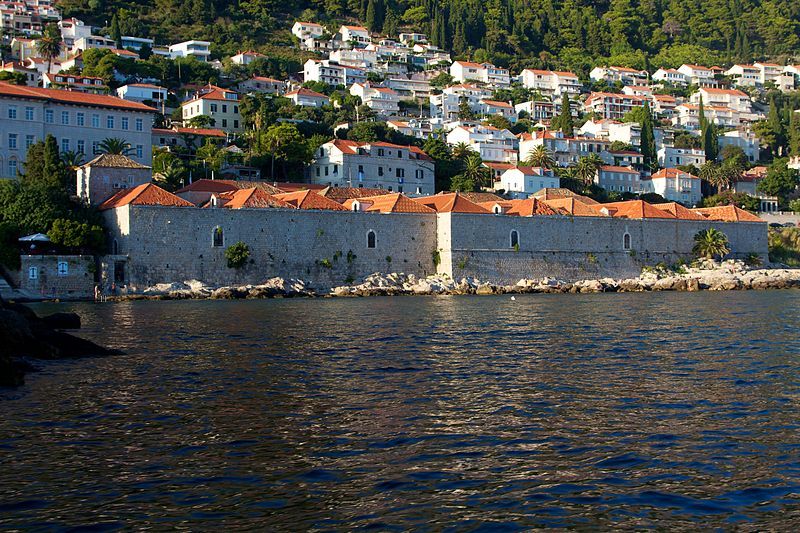
Lazarettos

Ramon
Lazarettos (Lazaretti)
This was the place for the first quarantine built in the fourteenth century in order to isolate travellers and goods from eastern countries. There were eight buildings and five courtyards which were renovated in the sixteenth century. This complex included large warehouses and lodging for the extended stay of merchants and travellers. In the seventeenth century, this was the largest merchant transit centre on the Adriatic and one of
the best-organised quarantines in the entire Mediterranean.
With this sheer amount of invaluable heritage that is still standing today after all these centuries, Dubrovnik definitely deserves to be considered one of the greatest towns in the world, and its popularity in terms of tourist visits and global interest is very much understandable.