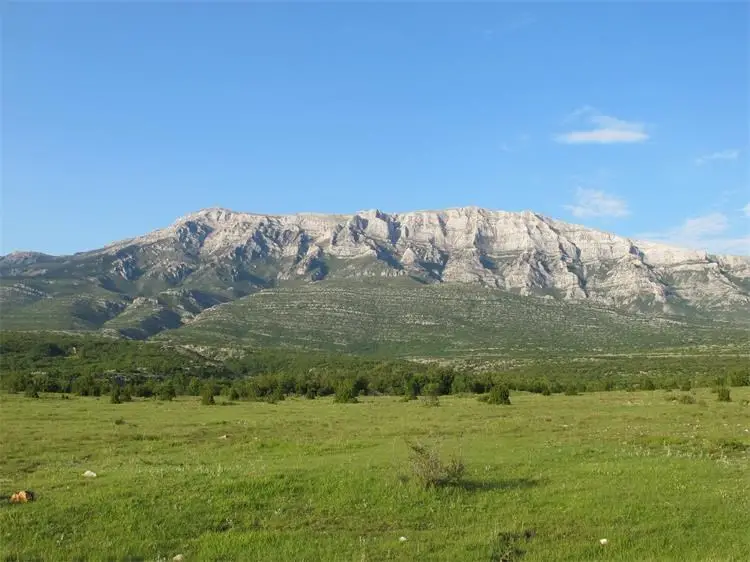
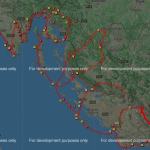
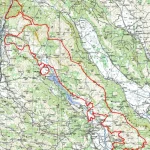
Today, the Croatian Parliament proclaimed the Mount Dinara Nature Park. The Park will encompass the area of the Dinara massif (Dinara, Troglav, and Kamešnica), the Cetina River’s upper course, and the Hrvatačko, Paško, and Vrličko karst fields. The highest peak of Croatia – Sinjal (1831 m), is located in the Park, too. These mountains are part of the Dinaric Alps, also commonly known as Dinarides, a mountain range in Southern and Southeastern Europe.
As the Minister of Economy and Sustainable Development Tomislav Ćorić said, the Mount Dinara Nature Park proclamation is an important moment for nature protection in Croatia, reports the Ministry.
“Mount Dinara Nature Park has become the 12th nature park in Croatia. Together with eight national parks, we have completed a set of 20 protected areas in the categories of nature and national parks,” said the Minister.
Source: Ministry of Economy and Sustainable Development
With an area of 63,052 ha, Mount Dinara Nature Park stretches through Šibenik-Knin and Split-Dalmatia counties. It is thus the second-largest nature park in Croatia, after Velebit Nature Park.
With the proclamation of Mount Dinara Nature Park, the share of protected areas in Croatia’s land area, together with the area of the ecological network Natura 2000, makes 39 percent of Croatia’s land area protected. There are 11 areas of the Natura 2000 ecological network in the Park area – two conservation areas important for birds and nine conservation areas important for species and habitat types.
The Park area is rich in other values derived from the centuries-old tradition of human use of space – semi-natural habitats, indigenous breeds and varieties, and rich cultural and historical heritage. The Dinaric karst is a phenomenon recognized at the international level that covers a much wider area, and it was named after the Dinara as a type locality.
Source: Ministry of Economy and Sustainable Development
Over 1000 plant species live here, a fifth of the total Croatian flora, and 75 of them are national endemics. Also, over 20 endemic animal species live in this area, and due to the untouched vast complexes of forests and grasslands, it is essential for our large carnivores – wolves, bears, lynxes. High Dinaric grasslands are the most important locality in Croatia for the yellow mountain viper (Vipera ursinii macrops), an endemic Dinarides snake species.
The protection of this area will have positive effects on nature conservation, but also the population and the economy of the wider region. The revitalization of extensive livestock is expected, as well as other traditional activities and new opportunities for sustainable use of space.
Source: Ministry of Economy and Sustainable Development
To read more news from Croatia, follow TCN’s dedicated page.